What would happen if you didn’t sleep? - Claudia Aguirre
TLDRIn 1965, Randy Gardner's 11-day sleep deprivation experiment revealed the severe consequences of sleeplessness, including hallucinations and memory impairment. Sleep is vital for adults and adolescents, with deprivation linked to hormonal imbalances, illness, and even death. Sleep-inducing chemicals like adenosine and melatonin initiate non-REM sleep, critical for DNA repair and body replenishment. The US faces a sleep-deprivation crisis, with significant percentages of adults and adolescents affected, leading to impaired learning, memory, mood, and reaction times. Chronic sleep deprivation can cause inflammation, hallucinations, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Fatal Familial Insomnia is a rare genetic condition causing perpetual wakefulness, leading to dementia and death. Scientists believe sleep deprivation's harm stems from the accumulation of waste products in the brain, which the glymphatic system clears more effectively during sleep. The lymphatic system in the brain may also aid in waste removal. As research continues, the necessity of sleep for health and mental well-being is undeniable.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Sleep is crucial for cognitive functions such as concentration and short-term memory.
- 👀 Randy Gardner's experiment showed that after 264 hours of sleep deprivation, he experienced mood swings, hallucinations, and paranoia.
- 🌙 Adequate sleep duration is vital; adults need 7-8 hours, and adolescents require about 10 hours per night.
- 🌗 Sleepiness is induced by a combination of body signals indicating tiredness and environmental cues like darkness.
- 🧪 The rise in chemicals like adenosine and melatonin helps us transition into sleep, which is essential for bodily repair and replenishment.
- 📉 In the U.S., a significant portion of adults and adolescents are regularly sleep-deprived, which can lead to serious health issues.
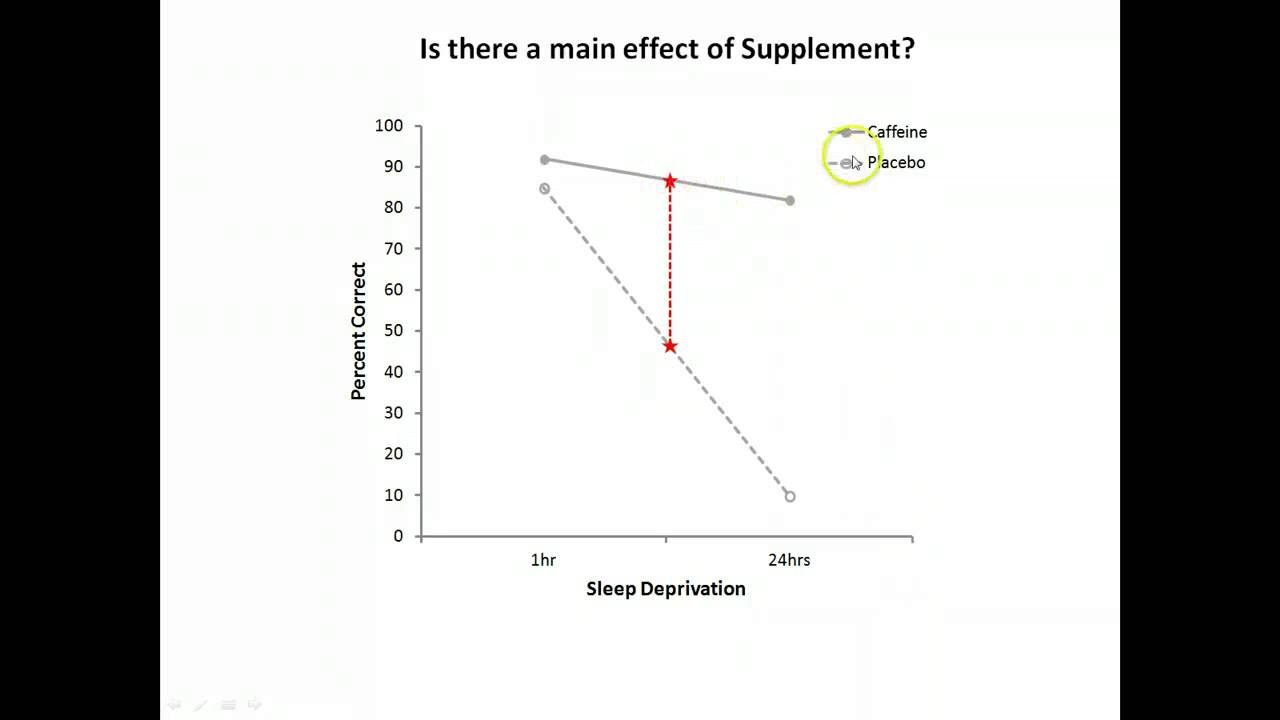
- 🚫 Lack of sleep can negatively impact learning, memory, mood, and reaction times, and may even cause inflammation and high blood pressure.
- 🏥 Fatal Familial Insomnia is a rare genetic condition that causes chronic sleeplessness, leading to dementia and death.
- ☕ Caffeine works by blocking adenosine receptors, which are associated with the urge to sleep.
- 🧫 The glymphatic system is a brain clean-up mechanism that is more active during sleep, removing waste products that accumulate between cells.
- 🧬 Scientists are still researching the restorative mechanisms of sleep, but it is clear that sleep is essential for maintaining health and sanity.
Q & A
What was the duration of Randy Gardner's experiment of staying awake?
-Randy Gardner stayed awake for 264 hours, which is equivalent to 11 days.
What were some of the physical and mental effects Randy Gardner experienced after the third day of staying awake?
-After the third day, Gardner became moody, uncoordinated, struggled to concentrate, had trouble with short-term memory, became paranoid, and started hallucinating.
What are the recommended hours of sleep for adults and adolescents according to the script?
-Adults need seven to eight hours of sleep a night, while adolescents require about ten hours.
How do our bodies signal that it is time to sleep?
-We grow sleepy due to signals from our body indicating we are tired, and environmental signals such as darkness outside, which lead to a rise in sleep-inducing chemicals like adenosine and melatonin.
What is the primary function of non-REM sleep?
-Non-REM sleep is when DNA is repaired, and our bodies replenish themselves for the day ahead.
What percentage of adults and adolescents in the United States are regularly sleep-deprived?
-It's estimated that 30% of adults and 66% of adolescents in the United States are regularly sleep-deprived.
What are some of the consequences of sleep deprivation on the body and mind?
-Sleep deprivation can affect learning, memory, mood, and reaction time. It may also cause inflammation, hallucinations, high blood pressure, and is linked to diabetes and obesity.
What is the connection between chronic sleep deprivation and stroke risk?
-Chronically sleeping fewer than six hours a night increases stroke risk by four and a half times compared to those getting a consistent seven to eight hours of sleep.
What is Fatal Familial Insomnia and how does it affect the body?
-Fatal Familial Insomnia is a rare genetic condition that places the body in a state of constant wakefulness, preventing sleep. This leads to a progressively worsening condition that results in dementia and death.
How does the accumulation of waste products in the brain contribute to the negative effects of sleep deprivation?
-The accumulation of waste products, such as adenosine, in the brain increases sleep pressure. If these waste products are not cleared away, they overload the brain and lead to the negative symptoms of sleep deprivation.
What is the glymphatic system and how does it help prevent the negative effects of sleep deprivation?
-The glymphatic system is a clean-up mechanism in the brain that removes waste buildup. It is more active during sleep and uses cerebrospinal fluid to flush away toxic byproducts that accumulate between cells.
What recent discovery in the brain may also play a role in clearing out the brain's daily waste products?
-Lymphatic vessels, which serve as pathways for immune cells, have recently been discovered in the brain and may also play a role in clearing out the brain's daily waste products.
Outlines
😱 The Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
In 1965, Randy Gardner, a 17-year-old, endured a sleep deprivation experiment by staying awake for 264 hours (11 days). The experiment revealed severe physical and psychological effects, such as loss of focus, inability to identify objects by touch, mood swings, impaired coordination, difficulty concentrating, memory issues, paranoia, and hallucinations. Despite Gardner's full recovery, the lack of sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances, illness, and even death in some cases. Sleep is crucial for adults, who need seven to eight hours per night, and for adolescents, who require about ten hours. The sleep process is triggered by signals from the body and environment, and involves the rise of sleep-inducing chemicals like adenosine and melatonin. Non-REM sleep is critical for DNA repair and body replenishment. Sleep deprivation is common, with 30% of adults and 66% of adolescents in the U.S. regularly not getting enough sleep, which can affect learning, memory, mood, and reaction times, and may even lead to inflammation, hallucinations, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Fatal Familial Insomnia is a rare genetic condition where individuals cannot sleep, leading to dementia and death. Scientists believe that the accumulation of waste products in the brain, such as adenosine, contributes to the negative effects of sleep deprivation. The glymphatic system, a cleanup mechanism, is more active during sleep and helps remove these toxic byproducts using cerebrospinal fluid. Recent discoveries of lymphatic vessels in the brain suggest they may also play a role in waste clearance. The importance of sleep for maintaining health and sanity cannot be overstated.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Sleep Deprivation
💡REM Sleep
💡Adenosine
💡Melatonin
💡Fatal Familial Insomnia
💡Glymphatic System
💡Lymphatic Vessels
💡Stroke
💡Paranoia
💡Hormonal Imbalance
💡DNA Repair
💡Sleep-Wake Cycle
Highlights
In 1965, Randy Gardner stayed awake for 264 hours to study the effects of sleep deprivation.
After 2 days, Gardner's eyes stopped focusing and he lost the ability to identify objects by touch.
By day 3, Gardner experienced moodiness and lack of coordination.
At the end of the experiment, Gardner struggled with concentration, short-term memory, paranoia, and hallucinations.
Gardner recovered fully, but sleep deprivation can cause hormonal imbalance, illness, and even death in extreme cases.
Adults need 7-8 hours of sleep per night, while adolescents require about 10 hours.
Sleepiness is induced by signals from our body and the environment indicating darkness.
Adenosine and melatonin are sleep-inducing chemicals that increase as we get tired.
Non-REM sleep is crucial for DNA repair and replenishing the body for the next day.
30% of US adults and 66% of US adolescents are regularly sleep-deprived.
Sleep deprivation can cause serious harm, affecting learning, memory, mood, and reaction time.
Lack of sleep may also lead to inflammation, hallucinations, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity.
A soccer fan died from a stroke after staying awake for 48 hours to watch the World Cup in 2014.
Chronic sleep deprivation (<6 hours per night) increases stroke risk by 4.5 times.
Fatal Familial Insomnia is a rare genetic condition causing relentless wakefulness, dementia, and death.
Sleep deprivation may cause immense suffering by accumulating waste products in the brain.
The glymphatic system is a cleanup mechanism in the brain that removes waste while we sleep.
Cerebrospinal fluid flushes away toxic byproducts that accumulate between brain cells during sleep.
Lymphatic vessels in the brain may also play a role in clearing out daily waste products.
Scientists continue to explore the restorative mechanisms of sleep, which is essential for maintaining health and sanity.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: