Space Compilation: Crash Course Kids
TLDRThis engaging script explores the wonders of space, focusing on our closest star, the Sun, and its importance to life on Earth. It delves into the vastness of the universe, introducing concepts like lightyears and the observable universe. The script also discusses the variety of stars, their classifications based on color and size, and the role of constellations in mapping the night sky. It highlights the Zodiac constellations and their significance in tracking the Sun's apparent path, known as the Ecliptic, throughout the year.
Takeaways
- 🌞 The closest star to Earth is the Sun, also known as 'Sol', which is the center of our solar system and provides energy crucial for life on Earth.
- 🌌 Space is vast and incomprehensibly large, with the universe being so massive that it's difficult for the human brain to fully grasp its scale.
- 📍 The observable universe is the part we can see or observe, with the limit being the distance light can travel in the available time since the Big Bang.
- 🌠 Stars vary in size, color, and temperature, with cooler stars glowing red and hotter stars glowing blue-white, and our Sun being a medium-temperature yellow star.
- 💫 Constellations are clusters of stars grouped together in patterns or shapes, with 88 recognized constellations many of which originated from ancient Greek mythology.
- 🐉 The Zodiac is a circle of constellations that the Sun appears to move through over the course of a year, with each of the 13 zodiac constellations visible during different months.
- 🛤️ The Ecliptic is the imaginary line created by the Earth's orbit around the Sun, which helps astronomers track the Sun's apparent path through the sky and is significant for understanding the visibility of the Zodiac constellations.
- 🚀 The concept of a light-year is used to measure vast distances in space, representing the distance light travels in one year at a speed of about 300,000 kilometers per second.
- 🌌 The universe is our home, and understanding its scale and the positions of celestial bodies within it can help us comprehend our place in the cosmos.
- 🌟 Stars like Betelgeuse and Rigel, part of the Orion constellation, demonstrate the variety in star types, with Betelgeuse being a cooler red supergiant and Rigel a hotter blue-white supergiant.
- 🌠 Ancient cultures have long used constellations for storytelling and navigation, and these patterns in the sky continue to be significant in modern astronomy and our understanding of the cosmos.
Q & A
What is the closest star to Earth?
-The closest star to Earth is the Sun, also known as Sol.
How old is the Sun?
-The Sun is approximately five billion years old.
What is the temperature at the core of the Sun?
-The core of the Sun is about 15 million degrees Celsius.
How long does it take for the energy created in the Sun's core to reach its surface?
-It can take over 100,000 years for energy to travel from the center of the Sun to its surface.
How long does it take for light from the Sun to reach Earth?
-Light from the Sun takes about eight minutes to travel to Earth.
What is the observable universe?
-The observable universe is the part of the universe that we can see or observe in any direction, limited by the speed of light and the age of the universe.
How big is the observable universe?
-The observable universe is approximately 93 billion lightyears across.
What is a light year?
-A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year, which is about 9.46 trillion kilometers or 5.88 trillion miles.
What are the two hottest stars in the constellation of Orion?
-The two hottest stars in the constellation of Orion are Betelgeuse and Rigel.
What is the difference between the colors of Betelgeuse and Rigel?
-Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star, which means it is cooler and glows red, while Rigel is a blue-white supergiant star, indicating it is hotter and glows blue-white.
What is the significance of constellations in astronomy?
-Constellations are clusters of stars that are grouped together in a pattern and given a name. They help astronomers map the night sky, find directions, and locate other celestial objects.
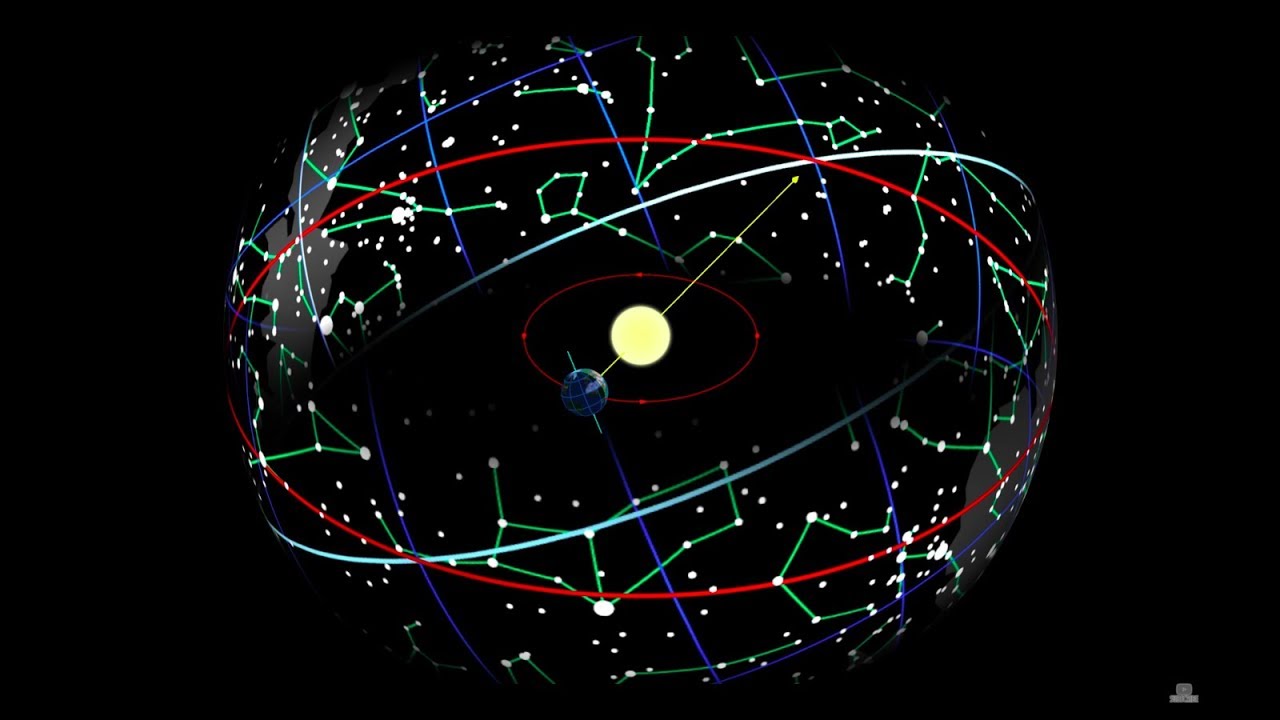
What is the Ecliptic?
-The Ecliptic is an imaginary line that represents the apparent path of the Sun through the Zodiac constellations over the course of a year, as a result of Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Outlines
🌞 Introduction to Space and Our Sun
This paragraph introduces the vast and awe-inspiring nature of space, emphasizing its coldness, vastness, and the wonders it holds. It highlights the importance of learning about space, particularly our own solar system and the Sun, which is revealed to be the closest star to Earth. The Sun, or 'Sol,' is described as a critical source of energy for our planet, with its size and temperature detailed. The paragraph explains the journey of the Sun's energy from its core to its surface, and then to Earth as light and heat, which takes approximately eight minutes. The Sun's role in sustaining life on Earth is underscored, and the paragraph concludes with a reflection on the importance of understanding our place in the universe.
🌌 The Immensity of the Universe
This paragraph delves into the sheer scale of the universe, challenging our comprehension with its vastness. It starts by establishing a cosmic address to contextualize our location within the universe, from the local studio to the observable universe. The concept of a light-year is introduced as a measure of distance, not time, and the speed of light is emphasized. The paragraph then uses a classroom-sized model to illustrate the relative scales of the Sun, Earth, and the entire solar system, emphasizing the minuscule size of our planet in comparison to the universe. It also touches on the observable universe's limits, as light from objects beyond this boundary has not yet reached us. The paragraph concludes with a reflection on the significance of our place in the universe, despite its overwhelming size.
🌠 Understanding Stars and Their Life Cycles
This paragraph focuses on the diversity and life cycles of stars, contrasting the Sun with other types of stars in the universe. It explains that stars are categorized by their color and size, which correlates with their temperature and the amount of energy they produce. The paragraph describes the surface temperatures of cool red stars and hot blue-white stars, positioning the Sun's temperature in the middle range. It also discusses the size variation among stars, from the smallest known to the largest that could extend beyond Saturn's orbit if placed in our solar system. The paragraph introduces two notable stars in the constellation Orion, Betelgeuse and Rigel, highlighting their different colors and stages in their stellar life cycles. The importance of understanding stars beyond their appearances is emphasized, as is the notion that stars, despite their vastness, have distinct 'personalities.'
🌟 Constellations and Their Significance
This paragraph explores the concept of constellations, which are clusters of stars grouped into patterns or shapes with specific names. It explains that constellations serve as navigational tools for astronomers, helping to map the night sky and locate less bright celestial objects. The paragraph discusses the origins of constellations in ancient Greek mythology, where they represented gods, creatures, and stories. It introduces several well-known constellations, including Draco, Hercules, Pegasus, and the Zodiac constellations, which are visible at different times throughout the year. The paragraph emphasizes the cultural and astronomical importance of constellations, noting that they have been studied for centuries and continue to be significant in our understanding of the cosmos.
📜 The Zodiac and the Ecliptic
This paragraph delves into the Zodiac, a specific group of 13 constellations that form a circular pattern in the sky and are associated with the path the Sun appears to follow throughout the year, known as the Ecliptic. The paragraph explains the concept of the Ecliptic as an imaginary line that tracks the Sun's apparent movement against the backdrop of the Zodiac constellations. It describes how the Earth's rotation and revolution around the Sun create the illusion of the Sun moving through these constellations. The paragraph lists each Zodiac constellation, providing a brief description and the associated mythological or symbolic significance. It concludes with a reflection on the importance of understanding the movements and positions of celestial bodies like the Sun and the stars in the context of the larger cosmos.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Space
💡Stars
💡Sun
💡Solar System
💡Constellations
💡Zodiac
💡Ecliptic
💡Light Year
💡Universe
💡Nuclear Fusion
💡Celestial Address
Highlights
Space is vast and inspiring, prompting us to learn more about it.
The closest star to Earth is the Sun, also known as Sol.
The Sun is a 5-billion-year-old ball of superhot gas, with a core temperature of about 15 million degrees Celsius.
Energy from the Sun's core takes over 100,000 years to reach its surface, then travels to Earth in about eight minutes as light and heat.
Without the Sun's energy, Earth would be a frozen, lifeless world.
The universe is so large that it's difficult for the human brain to comprehend.
Our observable universe is just a small part of the entire cosmos, with light from distant objects yet to reach us.
A light year is a measure of distance, representing how far light travels in one year.
The observable universe is 93 billion lightyears across.
Stars vary greatly in size, color, and temperature, and they go through life cycles similar to living organisms.
The hottest stars glow blue-white and can have surface temperatures over 30,000 degrees Celsius, while the coolest glow red and are around 2,760 degrees Celsius.
Constellations are clusters of stars in the sky grouped together in patterns or shapes and given names.
The ancient Greeks named many constellations after gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures.
The Zodiac is a circle of constellations that the Sun appears to move through over the course of a year, as observed from Earth.
The ecliptic is the imaginary line that represents the Sun's apparent path through the sky over the course of a year.
The Sun's position relative to the Zodiac constellations changes monthly, affecting our view of the night sky.
Understanding the cosmos, despite its vastness, is a fascinating journey of discovery.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: