🔌 Basic Electricity - What is voltage?
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concept of voltage in the context of basic electricity. It explains that voltage, measured in volts, is akin to a pushing force that drives the flow of electrons, creating an electric current. The video uses an adjustable power supply and an electric motor to demonstrate how increasing voltage leads to an increase in current and energy transfer. It further illustrates the use of voltage in powering devices and transmitting data, and clarifies that voltage is the difference in electrical potential energy per unit charge between two points, emphasizing its relativity and the importance of understanding this fundamental principle for grasping electrical systems.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Current is the flow of electrons in a wire, measured in amperes (amps).
- 🔌 Voltage is the force that pushes current around an electric circuit, like a battery.
- 📈 The more voltage applied, the more current flows through a circuit, as seen with the electric motor example.
- 💡 Voltage can be used to power devices like motors, light bulbs, and electronics.
- 📊 Voltage can also represent data in the form of electrical signals, such as in binary systems.
- 🔋 A battery creates voltage through a chemical reaction, which has more negative charge on one side, pushing electrons away.
- 🔄 The flow of electrons from the battery forms a complete circuit, allowing energy to be transferred.
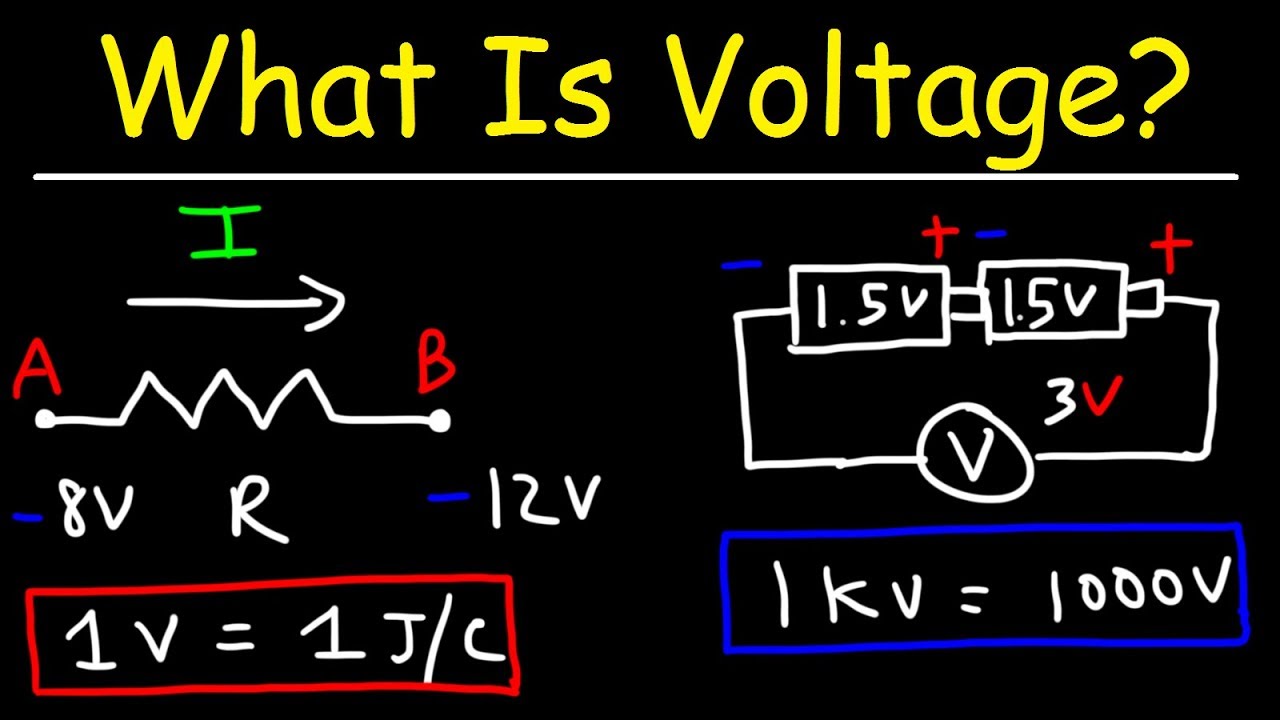
- 🔩 Voltage is the electrical potential energy difference per unit of charge between two points.
- ⚖️ The unit of charge is the coulomb, and 1 ampere equals 1 coulomb of charge flowing per second.
- 🔙 Voltage is always relative and measured between two points, also known as potential difference.
- 🚀 The higher the voltage, the more work a device can do, as seen with the motor spinning faster with increased voltage.
Q & A
What is the basic concept of current in electricity?
-Current, measured in amperes or amps, is the flow of electrons in a wire. It refers to the number of electrons passing a certain point per second.
What does voltage do in an electric circuit?
-Voltage pushes current around in an electric circuit, acting like a force that initiates the movement of electrons, thereby creating an electric current.
How does an adjustable power supply work?
-An adjustable power supply allows the creation of nearly any voltage desired, which is useful for designing circuits. It can also automatically measure the amount of current flowing through the circuit.
What happens when voltage is increased in a circuit?
-When voltage is increased, more current flows through the circuit. This results in more energy being transferred, which can cause devices like motors to operate faster or more efficiently.
What are some applications of voltage in electronics?
-Voltage can be used to power various devices such as motors, light bulbs, and other electronics. It can also be used to carry information through electrical signals representing data, like in binary communication systems.
What is the chemical process inside a battery that creates voltage?
-Inside a battery, there is a chemical reaction that creates a voltage. This reaction causes one side of the battery to be more negatively charged than the other, which in turn pushes electrons away and creates a flow of current in a complete circuit.
How is electrical potential energy defined and measured?
-Electrical potential energy is the ability of an electric charge to do work, such as moving or heating something. It is measured in joules, where 1 joule can power a flashlight for 1 second, and 90,000 joules can power a microwave for a minute to make tea.
What is the significance of the coulomb as a unit of charge?
-The coulomb is a standard unit of electric charge, with 1 coulomb equal to the charge of approximately 6.24 x 10^18 electrons. It simplifies calculations by allowing us to express current in terms of coulombs flowing per second instead of electrons.
How is voltage related to electrical potential energy and charge?
-Voltage is the electrical potential energy difference per unit of charge between two points. It represents the amount of energy transferred for every unit of charge that flows, such as 1.5 joules of energy for every coulomb of charge in a 1.5-volt battery.
Why is voltage always relative and measured between two points?
-Voltage, or electrical potential difference, is always relative because it represents the difference in potential energy between two points in a circuit. It is not an absolute value but rather a measure of the energy difference that drives the flow of electrons.
What are some alternative terms for voltage?
-Voltage is sometimes referred to as potential difference, tension, or electromotive force (EMF), which can lead to confusion but all essentially describe the same concept of electrical potential energy difference.
Outlines
🔋 Understanding Voltage and Current
This paragraph introduces the concept of voltage and its relationship with current. It explains that voltage, measured in volts, is the force that pushes electrons around an electric circuit, akin to a pushing force. The content includes a practical demonstration using an electric motor and an adjustable power supply to illustrate how varying voltage affects the amount of current flowing through the circuit. The paragraph also touches on the use of voltage in powering various devices and transmitting data through electrical signals.
🔌 Defining Voltage and Electrical Potential Energy
This paragraph delves into the scientific definitions of voltage and electrical potential energy. It clarifies that voltage is the difference in electrical potential energy per unit of charge between two points, and it is always relative. The explanation includes the concept of a coulomb as the standard unit of charge and how it relates to amps and joules. The paragraph uses the example of a battery to illustrate how chemical reactions create electrical potential energy, which is then converted into other forms of energy, such as light and heat, when current flows through a device. It emphasizes that voltage is about the transfer of energy per unit of charge and explains how this energy transfer is measured in joules.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡current
💡voltage
💡electric motor
💡power supply
💡electric circuit
💡chemical reaction
💡potential energy
💡joules
💡coulomb
💡binary
💡transmitter
Highlights
Voltage is the force that pushes current around an electric circuit.
An adjustable power supply can create nearly any voltage for circuit design.
Voltage can automatically measure the amount of current flowing in a circuit.
At zero volts, no current flows through the motor.
1 volt produces roughly 1.8 amps of current.
An increase in voltage results in more current flow and faster motor speed.
Voltage can power various devices like motors, light bulbs, and electronics.
Different voltages can represent binary data in a communication system.
Voltage is used not only to power high current devices but also as a signal with minimal current flow.
A battery creates voltage through a chemical reaction, causing electrons to move.
Voltage is a difference in electrical potential energy per unit of charge between two points.
Potential energy is the ability to do work, such as moving or heating something.
Energy is measured in joules, which can describe the amount of work done.
A coulomb is the standard unit of charge, making it easier to discuss current in terms of coulombs per second.
Voltage describes the energy transferred per unit of charge, like 1.5 joules per coulomb.
With a power supply at 1 volt, 1.8 joules of energy flow through the motor every second.
At 2 volts, 4 joules of energy flow through the motor every second, causing it to spin faster.
Voltage is always relative and measured between two points, also known as potential difference.
A 9-volt battery has a potential difference of 9 joules per coulomb between its terminals.
A 5-volt USB port has a rapidly changing 3.3 volts between its power pins for digital communication.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: