What is a Complex System?
TLDRThis transcript explores the concept of complex systems, highlighting the lack of a formal definition and the diverse perspectives on the topic. It presents a working definition, describing complex systems as collections of elements with relationships, where parts can be ordered or unordered. The emergence of global patterns from local interactions and self-organization is a key feature. The complexity arises from many distributed parts, hierarchical structure, interdependence, non-linearity, high connectivity, and the autonomy and adaptation of elements. These systems can shift rapidly, exhibit sensitivity to initial conditions, and adapt to their environment without centralized control, leading to a diverse and evolving macro scale organization.
Takeaways
- 📜 A complex system is a special class of system composed of elements and their relations.
- 🔍 The absence of a formal definition for complex systems leads to diverse perspectives on the subject.
- 🌐 In complex systems, elements can be ordered or unordered, affecting the system's overall functionality.
- 🌟 The emergence of a global pattern of organization from local interactions is a key characteristic of complex systems.
- 🔗 Complex systems are hierarchical, with elements nested within subsystems that form larger systems.
- 🔄 The interdependence and non-linearity of parts within a complex system can lead to synergistic effects or phase transitions.
- 🌐 High levels of interconnectivity in complex systems often present them as networks, redefining traditional concepts of space.
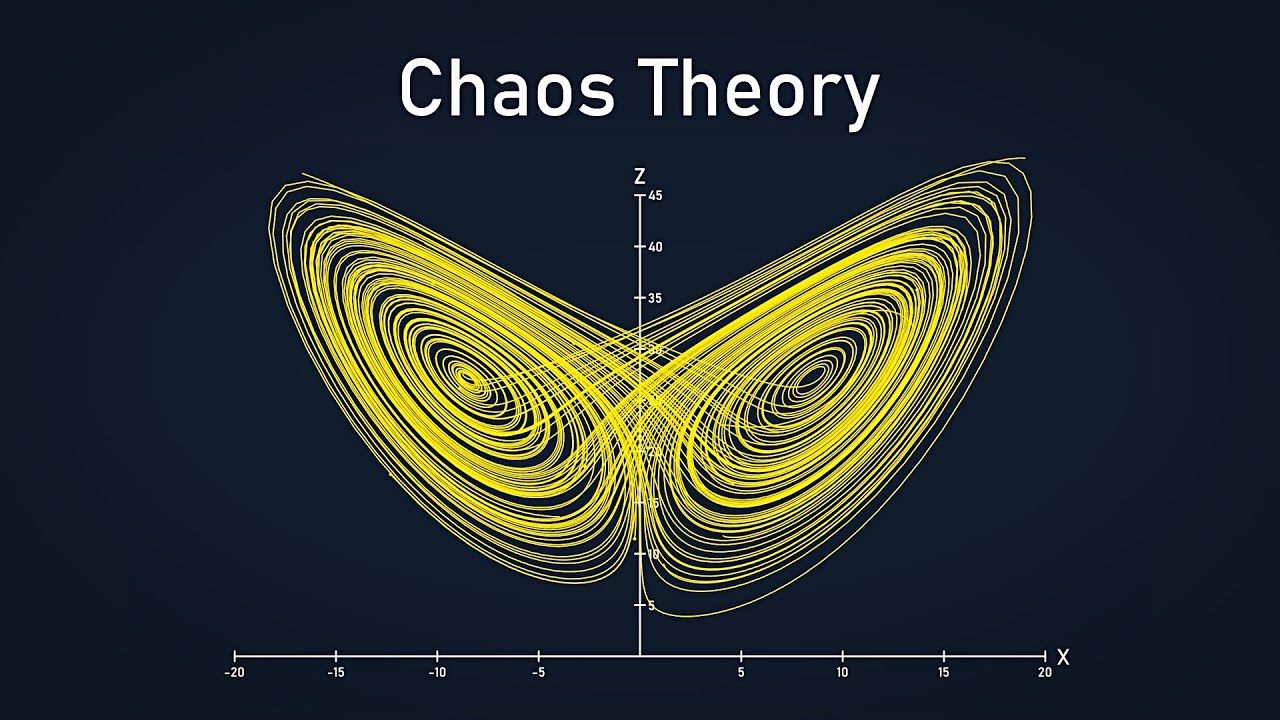
- 🦋 Sensitivity to initial conditions and the butterfly effect are examples of how small changes can lead to significant systemic impacts.
- 🤖 Autonomy and adaptation in complex systems enable self-organization and evolution without centralized coordination.
- 🌿 Heterogeneity and diversity are common in complex systems, contributing to their complexity and adaptability.
Q & A
What is the basic definition of a complex system?
-A complex system is a special class of system consisting of a set of parts (elements) and a set of connections (relations) between these parts. It can be ordered or unordered, and when elements are ordered, they can function together as a coherent whole, leading to the emergence of a new level of organization.
What is an example of an unordered system?
-A pile of stones on the ground is an example of an unordered set, as there is no specific structure or order to the system. It can only be described by listing its elements and their properties.
How does the concept of emergence work in complex systems?
-Emergence occurs when the elements of a complex system, working together, create a global pattern of organization that functions as a coherent whole. This new level of organization arises from the local interactions between the parts and self-organization processes.
What are the key properties of complex systems?
-Complex systems are characterized by many distributed parts without centralized control, self-organization, hierarchical structure, interdependence, non-linearity, high levels of connectivity, and elements with autonomy and adaptation capabilities.
How does non-linearity affect complex systems?
-Non-linearity means that the combined effect of the parts of a complex system may be greater or less than the simple sum of each part's properties in isolation. This is due to the interdependent nature of the elements and can lead to exponential relations between input and output, phase transitions, and sensitivity to initial conditions.
What is the significance of connectivity in complex systems?
-Connectivity is crucial in complex systems as it defines the nature and structure of the system. As connectivity increases, the system transitions from a set of parts to a network of connections, redefining space in terms of network topology and focusing on the flow of things within the network.
How does autonomy contribute to the complexity of a system?
-Autonomy allows elements within a complex system to adapt to their local environment and synchronize their states or cooperate without centralized coordination. This leads to the emergence of patterns of organization from the bottom up and enables the system to develop high levels of diversity and adaptability.
What is the role of adaptation in complex systems?
-Adaptation in complex systems refers to the process by which elements evolve according to their environment. This can occur through selection mechanisms such as market forces, voting in democracies, or natural selection in ecosystems, leading to the macro-scale system's ability to adapt and exhibit higher levels of differentiation and integration.
Why is there no formal consensus on the definition of a complex system?
-There is no formal consensus because complex systems are multifaceted and can be approached from various perspectives and disciplines. The diversity of opinions reflects the different ways in which researchers and scholars understand and study these systems.
How does the concept of hierarchy relate to complex systems?
-Hierarchy in complex systems refers to the nested structure where elements are part of subsystems, which in turn are part of larger systems. This multi-dimensional property means that complex systems are composed of many elements on different scales, all affecting each other.
What is the butterfly effect in the context of complex systems?
-The butterfly effect is a concept from chaos theory that suggests a small change in one part of a complex system can trigger a chain of events leading to large-scale consequences elsewhere in the system, due to sensitivity to initial conditions and feedback loops.
Outlines
🔍 Defining Complex Systems
This paragraph introduces the concept of complex systems, acknowledging the lack of a formal definition and the diverse perspectives on the subject. It presents a working definition where a complex system is a special class of system composed of elements and relations. The distinction between ordered and unordered systems is explained, using examples like a pile of stones versus a functioning car or a living organism. The paragraph emphasizes the emergence of a global pattern of organization from the local interactions of elements, leading to a coherent whole that is more than the sum of its parts.
🌐 Hierarchical Structure and Interdependence
The paragraph delves into the properties that define complex systems, highlighting the hierarchical structure where elements are nested within subsystems that form part of larger systems. It discusses the interdependence and non-linearity of parts within a complex system, which can lead to synergies or feedback loops that result in exponential relations between input and output. The concept of sensitivity to initial conditions and the butterfly effect are introduced, illustrating how small changes can lead to significant systemic effects. The paragraph also touches on the importance of connectivity in complex systems, where the nature and structure of connections define the system more than the properties of its components.
🤖 Autonomy, Adaptation, and Evolution
This paragraph concludes the discussion on complex systems by focusing on the autonomy and adaptation of elements within these systems. It explains how elements with a degree of autonomy can self-organize and evolve, leading to the emergence of patterns of organization from the bottom up. The paragraph also discusses the capacity for a variety of responses within complex systems due to their high levels of diversity. It wraps up by noting that complex adaptive systems evolve on the macro scale through processes such as natural selection, market forces, and democratic voting, allowing the system to adapt to its environment without centralized coordination.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Complex System
💡Emergence
💡Hierarchy
💡Non-linearity
💡Feedback Loops
💡Connectivity
💡Autonomy
💡Adaptation
💡Diversity
💡Self-Organization
💡Evolution
Highlights
Complex systems have no formal definition, but are characterized by multiple perspectives and opinions.
A complex system is a special class of system consisting of elements and relations between these parts.
In unordered systems, elements have no specific structure or order, and can be described by listing their properties.
Ordered systems function together as a whole, with the emergence of a global pattern of organization.
Complex systems are characterized by many parts distributed without centralized control and self-organization.
The phenomenon of emergence leads to new levels of organization within complex systems.
Complex systems exhibit a hierarchical structure with elements nested inside subsystems and larger systems.
Interdependence and non-linearity in complex systems create feedback loops and synergies.
Non-linearity can result in exponential relations between input and output, leading to phase transitions.
Complex systems often involve dense interconnectivity, which redefines the traditional conception of space.
Autonomy and adaptation in complex systems enable self-organization and evolution.
Elements within complex systems can synchronize states locally or cooperate, leading to emergent patterns.
Complex systems are heterogeneous, with high levels of diversity and the capacity for varied responses.
Evolutionary forces shape complex systems on a macro scale without centralized coordination.
Complex systems adapt to their environment and exhibit higher levels of differentiation and integration.
The autonomy and adaptation capacity of elements within a system contribute to the system's complexity.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: