The Nucleus: Crash Course Chemistry #1
TLDRHank Green aims to convince viewers that chemistry is an amazing science that helps us understand the world. He traces the history of atomic theory, highlighting key figures like Robert Brown and Einstein, who proved atoms exist. Atoms, made of protons, neutrons, and electrons, combine in different ways to form all matter. The number of protons defines an element, while isotopes have the same chemical properties but different masses. Nuclei are boring; electrons do the interesting chemical stuff. Understanding chemistry, according to Hank, helps us better enjoy the mysteries of the universe.
Takeaways
- 😀 Atoms were finally confirmed to exist when Einstein mathematically defined Brownian motion in 1905
- 👨🔬 Elements are chemically pure substances defined by the number of protons (atomic number) in their nuclei
- 👍 Neutrons stabilize atom nuclei by spacing out the protons
- 🚜 Different isotopes of elements cause their relative atomic masses to not be whole numbers
- 😴 Atom nuclei are boring - electrons do all the interesting chemistry
- 📚 Silver's chemical symbol Ag comes from the Latin word 'argentum' meaning shiny gray stuff
- 🔬 The strong nuclear force holds together protons and neutrons in nuclei
- 🌡️ Electrons determine how an atom behaves chemically by what they are bonded to
- ⚛️ Chemistry explains the properties and behaviors of all physical stuff, which is made of atoms
- 💡 Understanding chemistry leads to a deeper understanding of the world
Q & A
What discovery led to the mathematical proof for the existence of atoms and molecules?
-In 1905, Albert Einstein mathematically proved the existence of atoms and molecules when he theorized that the random motion of pollen grains in water, known as Brownian motion, was caused by atomic particles colliding with them.
What are the three subatomic particles that make up an atom?
-The three subatomic particles that make up an atom are: the proton, which is heavy and positively charged; the neutron, which is about the same size as a proton but has no charge; and the electron, which has negative charge and very little mass.
What feature of an atom determines what element it is?
-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines what element it is. This number is called the atomic number.
Why doesn't silver have the chemical symbol Si or Sv?
-Silver was one of the first elements added to the periodic table and at that time it was called 'argentum', Latin for 'shiny gray stuff'. So silver was given the chemical symbol Ag, from argentum. The name stuck even though it doesn't actually represent the element.
What are isotopes and why do they cause relative atomic masses to not be whole numbers?
-Isotopes are variants of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Since isotopes of the same element exist in nature, the relative atomic mass ends up being an average across all isotopes, causing it to be a decimal number rather than a whole number.
What does the atomic number represent and why is it important?
-The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. It determines what element an atom is and is the defining, unchanging characteristic across all isotopes and chemical reactions.
What is the purpose of neutrons in an atomic nucleus?
-Neutrons act as a buffer between protons in the nucleus. They allow the protons to be packed together more densely by spacing them out, preventing the positively charged protons from repelling each other.
What are the two acceptable pronunciations for the word "nucleus"?
-The two acceptable pronunciations for the word "nucleus" are "nuculus" and "nucleus".
Where in an atom do chemical reactions take place?
-Chemical reactions involve the electrons surrounding an atom's nucleus. The nucleus remains stable throughout chemical changes.
How did the discovery of atoms change our understanding of matter?
-The realization that all physical things are made up of discrete building blocks called atoms revolutionized our conceptualization of matter, transforming alchemy into the science of chemistry.
Outlines
🤓 Intro to Chemistry and Atoms
Hank Green introduces chemistry as the science of stuff and how atoms combine to form everything. He talks about the history of atomic theory and how Einstein mathematically proved atoms exist by explaining Brownian motion. Hank also covers basics like protons, neutrons, and electrons, as well as atomic number, isotopes, and more.
🤨 Why the Symbol for Silver is Ag
Hank explains that silver's chemical symbol Ag comes from the Latin word "argentum" meaning shiny gray stuff, which is also the root of the country name Argentina. He then returns to discussing atomic nuclei, neutrons, and isotopes.
🙌 Thank You for Watching!
Hank concludes the video by thanking viewers for watching the first episode of Crash Course Chemistry.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡atoms
💡elements
💡atomic number
💡isotopes
💡nucleus
💡neutrons
💡electrons
💡protons
💡relative atomic mass
💡mass number
Highlights
Atoms were finally confirmed when Einstein mathematically defined Brownian motion
Elements are chemically pure substances, and the type of element an atom is is defined by how many protons it has in its nucleus, or its atomic number
Neutrons stabilize nuclei for their proton friends
Different isotopes of the same element are the reason relative atomic masses are never whole numbers
Nuclei are the uninteresting, boring bits of the atom, and the electrons are where all the interesting chemical stuff happens
All stuff is made from atoms - tiny discrete particles that have specific properties depending on the arrangement of three simple subatomic particles
The number of protons in an element determines what element it is
Neutrons serve as a buffer between the protons in the nucleus
Isotopes have different masses but the same chemical properties, and are the same element
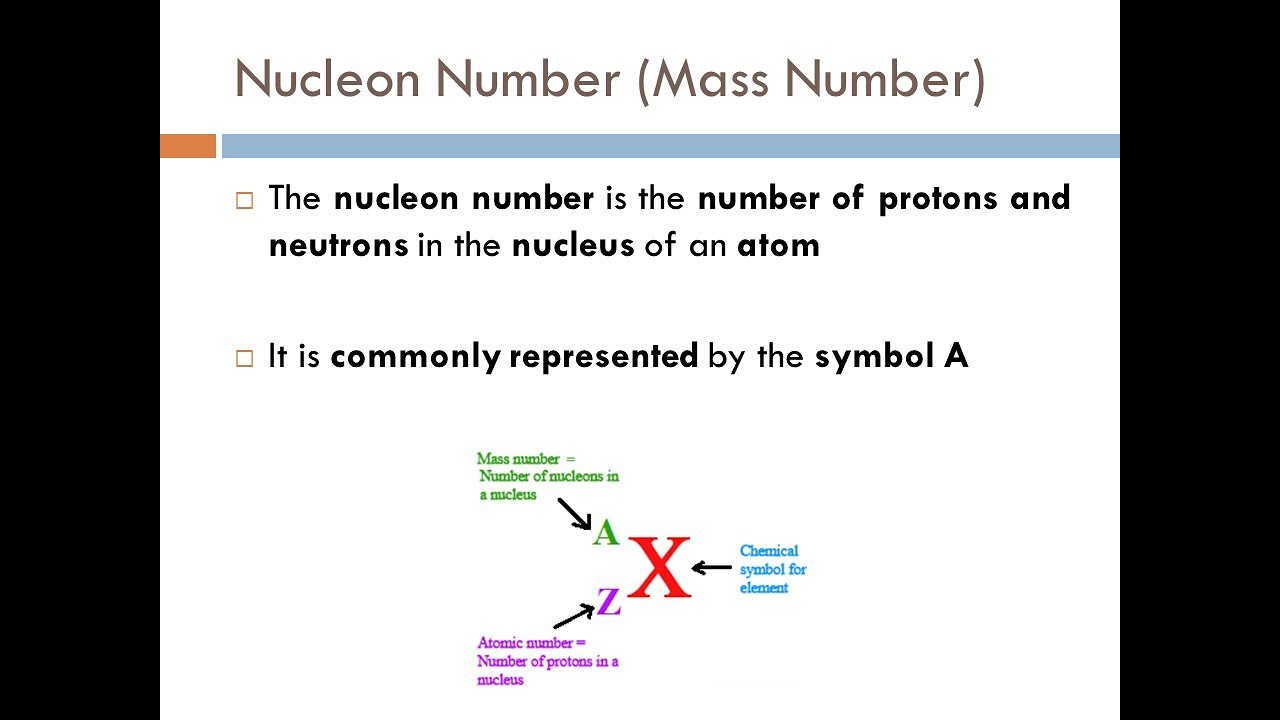
The mass number is the total number of nucleons in the nucleus
Atomic theory sounded crazy when first proposed, but Einstein's work on Brownian motion proved it
The periodic table sits right on top of the box because the atomic number is the defining trait
Silver's chemical symbol Ag comes from the Latin word for shiny gray stuff, argentum
Nuclei are held together by the strong nuclear force, the strongest of the four fundamental forces of physics
The relative atomic mass is the number of protons plus neutrons, averaged for all atoms of an element on Earth
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

GCSE Chemistry - Elements, Isotopes & Relative Atomic Mass #2

What Is An Atom - Part 1 | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

What are Isotopes? | Chemistry
Learning Outcomes (d) and (e) from Atomic Structure - JC H2 Chemistry

What are Isotopes? | Chemistry Basics

What Are Radioactive Isotopes (radionuclides) | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: