What is ACID RAIN? | Acid Rain | Dr Binocs Show | Kids Learning Video | Peekaboo Kidz
TLDRThis video explores the alarming phenomenon of acid rain, a result of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide reacting with atmospheric water and oxygen. It explains the natural and human-induced sources of these gases, and how they form acids that significantly lower the pH of rain. The script delves into the ecological impact of acid rain on aquatic life, forests, and even buildings, highlighting the urgency of reducing fossil fuel consumption to mitigate its effects. The video concludes with a call to action to spread awareness and protect our environment.
Takeaways
- 🌧️ Acid rain is a real environmental phenomenon and is not a fictional story.
- 💧 Rain clouds are typically composed of pure water, but can become acidic when they chemically react with sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide in the atmosphere.
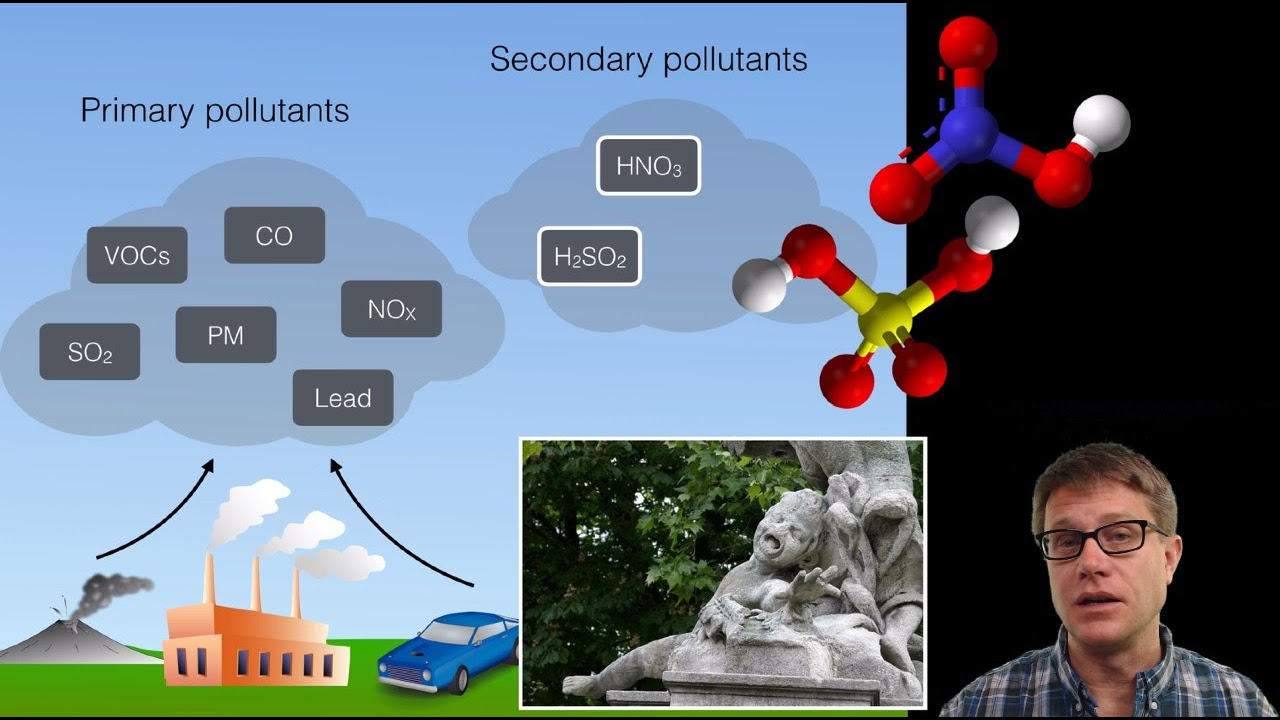
- 🌊 Wet deposition refers to acid rain that contains water, while dry deposition involves acid rain formed with dust or gases.
- 🌿 Natural sources of acid rain include rotting vegetation and volcanic eruptions, but human activities such as burning fossil fuels are the primary cause.
- 🔥 The burning of fossil fuels releases gases like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which are major contributors to acid rain.
- 🌧️ Normal rain is slightly acidic with a pH of about 6 due to the dissolution of carbon dioxide, forming carbonic acid.
- ⚗️ Acid rain has a significantly lower pH, around 3, which makes it much more acidic than normal rain.
- 🌳 Acid rain has ecological effects, particularly harming aquatic environments by increasing water toxicity and aluminum absorption.
- 🌲 It also damages forests by stripping leaves and soil of essential nutrients, affecting tree health.
- 🏛 Acid rain can damage buildings, monuments, and statues, especially those made of limestone and marble, due to their calcium carbonate content.
- 🛑 To combat acid rain, reducing the burning of fossil fuels is crucial, as well as spreading awareness about its effects.
Q & A
What is acid rain and why is it a concern?
-Acid rain is a form of precipitation that has a higher than normal acidity due to the presence of certain pollutants in the atmosphere, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide. It's a concern because it can harm the environment, including aquatic ecosystems and forests, and damage buildings and monuments.
How does acid rain form?
-Acid rain forms when gases like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide chemically react with water and oxygen in the atmosphere. These reactions produce acids that mix with rainwater, leading to a lower pH and increased acidity.
What is the difference between wet and dry deposition in the context of acid rain?
-Wet deposition refers to the acid rain that falls directly as precipitation, while dry deposition refers to acidic particles or gases that settle on surfaces without the presence of rain.
What are the natural sources of the gases that contribute to acid rain?
-Natural sources of these gases include the decomposition of vegetation and volcanic eruptions, which release chemicals that can contribute to acid rain.
What are the main human activities that contribute to the formation of acid rain?
-Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, emissions from vehicles, and chemicals released from factories are the main contributors to the formation of acid rain.
Why is normal rain slightly acidic?
-Normal rain is slightly acidic because as it falls, it dissolves carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, forming carbonic acid with a pH of about 6.
What is the pH level of acid rain and how does it compare to normal rain?
-Acid rain has a pH level of about 3, which is significantly lower and more acidic than normal rain.
How does acid rain affect aquatic life?
-Acid rain makes waters more acidic, leading to increased aluminum absorption from the soil, which is toxic for aquatic animals and can disrupt their habitats.
What impact does acid rain have on forests?
-Acid rain can damage leaves and strip the soil of essential nutrients, making it difficult for trees to absorb water and potentially harming the overall health of the forest.
What are some steps that can be taken to reduce acid rain?
-Reducing the burning of fossil fuels and raising awareness about the issue are two steps that can be taken to help mitigate the effects of acid rain.
How does acid rain affect buildings, monuments, and statues, especially those made of limestone and marble?
-Acid rain can damage these structures by reacting with the calcium carbonates they contain, leading to chemical reactions that can change their appearance and cause deterioration.
Can you provide an example of how acid rain has affected a historical monument?
-The Taj Mahal in Agra was greatly affected by exhaust gases from the Mathura refinery, which caused significant discoloration due to acid rain.
Outlines
🌧️ Understanding Acid Rain
This paragraph introduces the concept of acid rain, explaining its formation through the chemical reaction of gases like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide with water and oxygen in the atmosphere. It distinguishes between wet and dry deposition, and highlights the main sources of these gases, which include natural processes and human activities such as burning fossil fuels and industrial emissions. The paragraph also clarifies the difference between normal rain's slight acidity and the significantly higher acidity of acid rain, which can have a pH as low as 3. An example is provided to illustrate how sulfur in plants can end up in the atmosphere as sulfur dioxide when fossil fuels are burned, contributing to acid rain.
🌳 Ecological Impacts and Solutions for Acid Rain
The second paragraph delves into the ecological effects of acid rain, particularly its impact on aquatic life in lakes and rivers, where increased acidity and aluminum absorption can be toxic to aquatic animals. It also discusses the damage acid rain can cause to forests by leaching essential nutrients from the soil and harming leaves. The paragraph suggests reducing the burning of fossil fuels as a primary solution to mitigate acid rain and emphasizes the importance of spreading awareness about the issue. Additionally, it mentions the damage acid rain can cause to buildings, monuments, and statues, especially those made of limestone and marble, providing the example of the Taj Mahal's discoloration due to exhaust gases from a nearby refinery.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Acid Rain
💡Wet Deposition
💡Dry Deposition
💡Sulfur Dioxide
💡Nitrogen Oxide
💡Carbon Dioxide
💡pH
💡Ecological Effects
💡Fossil Fuels
💡Aluminum Absorption
💡Calcium Carbonates
Highlights
Acid rain is a real environmental phenomenon with serious consequences.
Rain clouds, typically pure water, can become acidic through chemical reactions with sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide.
Acid rain is categorized into wet deposition (rain with water) and dry deposition (with dust or gases).
Natural sources like rotting vegetation and volcanic eruptions contribute to acid rain, but human activities are the primary cause.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, vehicle emissions, and factory chemicals, are major contributors to acid rain.
Normal rain is slightly acidic due to the formation of carbonic acid when rainwater dissolves carbon dioxide.
Acid rain has a significantly lower pH, around 3, compared to normal rain, due to stronger acids from pollutants.
An example explains how plants absorb sulfur, which later contributes to acid rain when fossil fuels are burned.
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide in the atmosphere react with oxygen to form sulfuric and nitric acids, respectively.
Acid rain has ecological effects, particularly harming aquatic life by increasing water toxicity.
Acid rain also damages forests by leaching essential nutrients from the soil and harming leaves.
Reducing the burning of fossil fuels is a practical step to mitigate the effects of acid rain.
Spreading awareness about acid rain through education can help combat this environmental issue.
Acid rain can damage buildings, monuments, and statues, especially those made of limestone and marble.
The Taj Mahal at Agra was affected by exhaust gases from a nearby refinery, illustrating the impact of acid rain on cultural heritage.
Dr. Bynox encourages viewers to subscribe and stay informed about environmental topics.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: