AP World History (WHAP) 1900-1945 TikTok Review: World War I and II
TLDRThis script provides an insightful overview of World War I and II, discussing the long-term causes, including industrialization, nationalism, and complex alliances. It highlights key events like the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and the United States' late entry into WWI. The script also touches on the Treaty of Versailles' shortcomings and the rise of WWII, marked by aggressive expansion by Germany and Japan, and the policy of appeasement. It concludes with the major impacts of WWII, such as the decline of European imperialism, the onset of the Cold War, and the emergence of new global powers.
Takeaways
- 🏭 Industrialization was a key context for World War I, driving competition and imperialism among European states.
- 🌏 Imperialism led to tensions as nations expanded and their interests clashed, particularly in the Balkans and overseas colonies.
- 🔫 Militarization increased as countries built up their armed forces, which in turn heightened tensions and contributed to the complex web of alliances.
- 🏰 Nationalism played a significant role, with each nation believing in its superiority and right to dominate.
- 🔗 Alliances formed a complex system that, when triggered by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, led to the outbreak of World War I.
- 🇷🇸 The assassination of Franz Ferdinand by a Serbian nationalist was the immediate cause that set off a chain reaction of events leading to the war.
- 💥 World War I was characterized by trench warfare, where advanced technology outpaced military strategy, leading to devastating losses.
- 📜 The Treaty of Versailles and other peace treaties post-WWI created more problems than they solved, sowing the seeds for future conflicts.
- 🌍 World War II was influenced by unresolved tensions post-WWI, the rise of aggressive powers like Germany and Japan, and policies of appeasement by other powers.
- 🗽 The United States' entry into World War I and later World War II were pivotal moments that shifted the balance of power and contributed to the end of both wars.
- 🕊️ Post-WWII, there was a significant decline in European imperialism, leading to decolonization and the rise of the U.S. and Soviet Union as superpowers, which marked the beginning of the Cold War era.
Q & A
What is the acronym 'M.A.I.N.E.S.' used to represent the main causes of World War One?
-The acronym 'M.A.I.N.E.S.' stands for Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, Nationalism, and Economic rivalries. These factors contributed to the long-term causes of World War One.
How did industrialization contribute to the tensions leading up to World War One?
-Industrialization led to increased competition among European states, as they sought to expand their empires and secure resources. This also resulted in the modernization and build-up of militaries, causing tensions due to the fear and suspicion of other nations' intentions.
What was the significance of the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand?
-The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Gavrilo Princip, a member of the Black Hand organization, was the immediate trigger for World War One. It set off a chain reaction of events due to the complex system of alliances, leading to a full-scale war.
Why did the United States enter World War One in 1917?
-The United States entered World War One in 1917 partly due to fear that with Russia's withdrawal from the war, Germany could focus its forces on the Western Front, and also due to unrestricted submarine warfare by Germany that threatened American lives and interests.
What was the impact of the Treaty of Versailles on post-World War One Europe?
-The Treaty of Versailles had a significant impact on post-World War One Europe by imposing harsh penalties on the Central Powers, leading to economic and political instability. It also created resentment and set the stage for the rise of extremist ideologies.
How did World War One lead to the rise of the League of Nations?
-The League of Nations was established after World War One with the intention of preventing future conflicts through collective security and disarmament. However, it was weakened by the absence of key players like the United States and the dissatisfaction of various nations with the peace process.
What were the two main factors that contributed to the outbreak of World War Two?
-The two main factors that contributed to the outbreak of World War Two were the aggression by Germany and Japan, as they sought to expand their empires, and the policy of appeasement by other powers, which allowed their aggressive actions to go unchecked.
Why did the policy of appeasement fail to prevent World War Two?
-The policy of appeasement failed to prevent World War Two because it emboldened aggressive nations like Germany and Japan, who interpreted the lack of resistance as weakness and continued their expansionist policies, ultimately leading to the war.
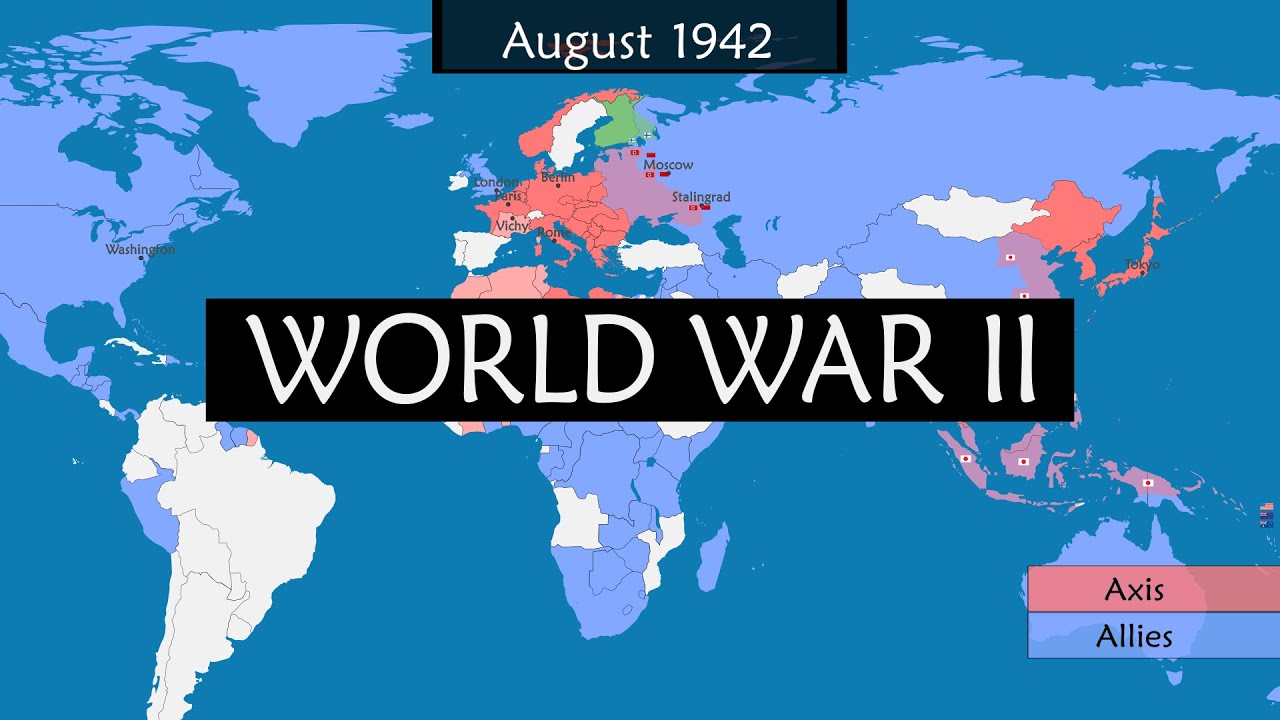
What was the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad during World War Two?
-The Battle of Stalingrad was significant as it marked a major turning point on the Eastern Front of World War Two. The Soviet Union's victory halted the German advance into the Soviet Union and began the process of pushing the Germans back.
How did the outcomes of World War Two lead to the Cold War?
-The outcomes of World War Two, particularly the decline of European imperialism and the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, set the stage for the Cold War. The ideological differences and geopolitical tensions between these two powers led to a prolonged period of conflict and competition.
What were the major impacts of World War Two on global politics and society?
-The major impacts of World War Two included the decline of European imperialism and the onset of decolonization, the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers leading to the Cold War, and the catalyst for modern rights movements and global political realignments.
Outlines
🌟 Origins and Causes of World War I
This paragraph delves into the long-term causes leading up to World War I, highlighting the role of industrialization, competition, imperialism, militarization, and nationalism. It explains how these factors contributed to a complex web of alliances. The precipitating event is the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Gavrilo Princip, a Serbian nationalist, which set off a chain of events involving alliances and declarations of war, ultimately leading to the global conflict. The paragraph also touches on the nature of warfare during WWI, characterized by trench warfare and technological advancements that outpaced military strategy.
🔥 The Course and Aftermath of World War I
This section outlines the key events and turning points of World War I, including the Russian Revolution and the United States' late entry into the war, which helped tip the balance. It discusses the Treaty of Versailles and its negative repercussions, creating resentment and laying the groundwork for future conflicts. The paragraph also covers the post-war tensions and the establishment of the League of Nations, which was ultimately ineffective in preventing World War II. The summary concludes with the rise of aggressive powers like Germany and Japan, and the policy of appeasement by other nations, setting the stage for the next global conflict.
🌍 World War II: The Global Conflict and Its Impact
This paragraph provides an overview of World War II, starting with Hitler's invasion of Poland and moving through key battles and strategies such as the Battle of Midway, the Battle of Stalingrad, and the island-hopping campaign in the Pacific. It discusses the use of atomic bombs on Japan and the subsequent division of Germany and Berlin. The summary also addresses the post-war outcomes, including the decline of European imperialism, the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, and the onset of the Cold War. The paragraph concludes by connecting World War II to broader historical trends such as decolonization and the emergence of modern rights movements.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡World War One
💡Industrialization
💡Militarism
💡Nationalism
💡Alliances
💡Assassination of Franz Ferdinand
💡Trench Warfare
💡Russian Revolution
💡United States Entry
💡Versailles Treaty
💡Decolonization
💡Cold War
Highlights
Introduction to the long-term causes of World War One using the acronym MAINE.
Importance of industrialization in the context of World War One as it ramped up competition and imperialism.
Militarization due to industrialization leading to tensions in Europe and the build-up of modern armies.
Nationalist sentiment as a cause for World War One, with the belief in national superiority.
Complex system of alliances formed due to the tensions between European states.
The precipitating event of World War One: the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
Alliances leading to a chain reaction of declarations of war, starting with Austria-Hungary and Serbia.
The role of Belgium's neutrality in bringing England into the conflict.
World War One as a truly global conflict, with fighting centered in Europe and involving colonies.
Trench warfare as a result of advanced technology outpacing military strategy.
The turning point of World War One in 1917 with the Russian Revolution and US entry into the war.
The Treaty of Versailles as the 'worst peace treaty of all time' creating more problems than it solved.
Post-World War One tensions and the weaknesses of the League of Nations in preventing future conflicts.
Aggression by Germany and Japan as key factors leading to World War Two.
Appeasement policies by other powers, such as Britain and the US, inadvertently encouraging aggression.
Major battles and turning points of World War Two, including the Battle of Stalingrad and the Battle of Midway.
The outcomes of World War Two, including the decline of European imperialism and the rise of the US and Soviet Union as superpowers.
The impact of World War Two on the Cold War, decolonization, and modern rights movements.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: