TYPES OF FORCES | SCIENCE | GRADE 3 | The Study Pod
TLDRThis educational video introduces various types of forces, including magnetic force, electric force, gravity, and friction. It explains how magnetic forces attract or repel objects based on their poles, and demonstrates electric force through an experiment with a balloon and hair or paper. The video also discusses gravity as the force that pulls objects towards Earth, causing them to fall, and highlights the role of friction in slowing down and stopping motion. The script aims to engage young learners with hands-on examples and encourages questions for further exploration.
Takeaways
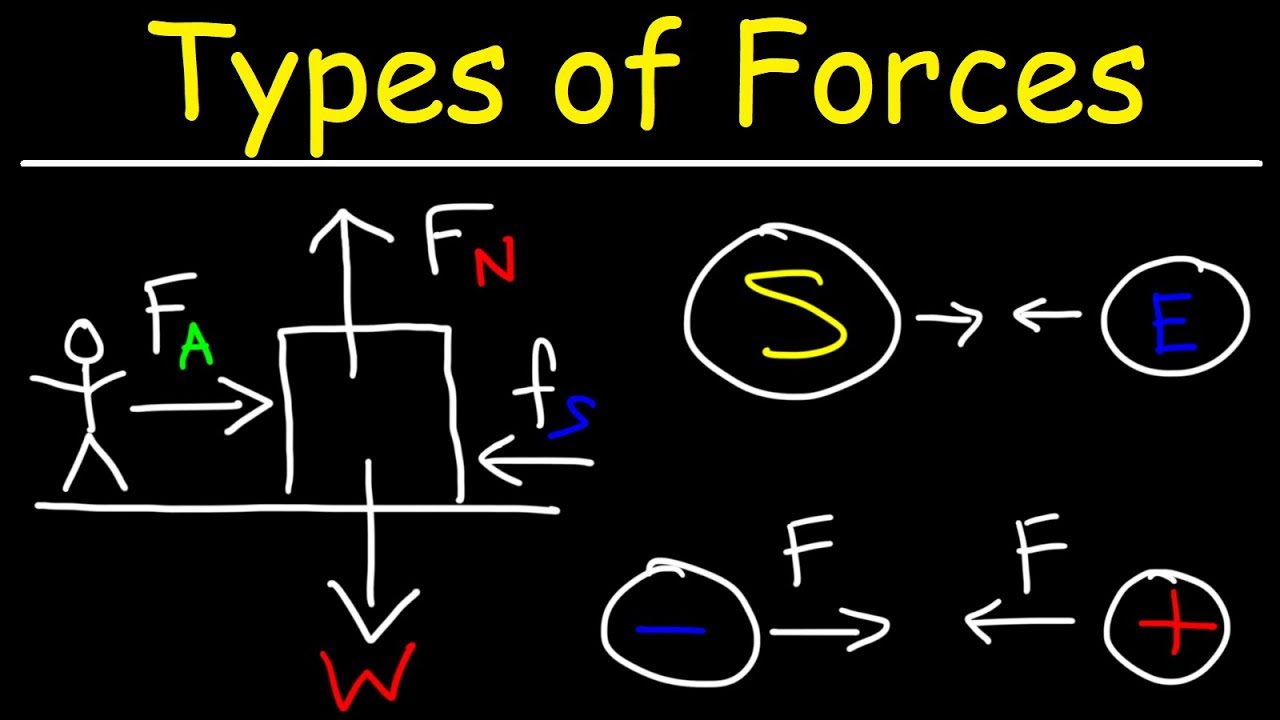
- 🧲 The magnetic force is a non-contact force that can attract objects made of materials like iron and steel.
- 🧲🔧 A magnet has two poles, a south and a north, and unlike poles attract each other while like poles repel each other.
- 🔋 When a balloon is rubbed on clothes, it becomes electrically charged and can attract small, light objects due to the electric force.
- 🌍 The gravitational force, or gravity, is the force of attraction between the Earth and objects near its surface, causing them to fall back to the ground.
- 🌌 In space, the absence of gravity allows astronauts and objects to float because there is no force of attraction pulling them towards a celestial body.
- 🏀 When a ball bounces and eventually stops, it's due to the frictional force acting against its motion, causing it to slow down and eventually come to rest.
- 🔄 Friction is a contact force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact and acts in the opposite direction to the motion.
- 👟 Friction is essential for walking; without it, we would slip because there would be too little resistance between our shoes and the ground.
- 🔬 An experiment with a sweater and a balloon demonstrates the concept of electric charge and how it can attract objects.
- 📚 The video script introduces and explains four different types of forces: magnetic, electric, gravitational, and frictional forces.
- ✉️ For any questions or queries about the content, viewers are encouraged to reach out via email to studypod01@gmail.com.
Q & A
What are the different types of forces mentioned in the video script?
-The different types of forces mentioned in the video script are magnetic force, electric force, gravity, and friction.
How does a magnetic force attract objects?
-A magnetic force can attract objects made of materials such as iron and steel by pulling these objects towards the magnet. It is a non-contact force, meaning it can act without touching the object.
What are the two poles of a magnet and how do they interact with each other?
-A magnet has two poles: a south pole and a north pole. Unlike poles of magnets can attract each other, while like poles repel each other by pushing each other away.
What is the term used for the pull of a magnet?
-The pull of a magnet is called the magnetic force of attraction.
What happens when you rub a balloon on a sweater and bring it near your hair or small pieces of paper?
-When you rub a balloon on a sweater and bring it near your hair or small pieces of paper, the balloon, which has become electrically charged, will attract the hair or paper due to the electric force between the charges.
What is the force that causes a thrown ball to fall back to the ground?
-The force that causes a thrown ball to fall back to the ground is called gravitational force or gravity, which is the force of attraction between the Earth and any object near its surface.
Why do astronauts and other objects float around in space?
-Astronauts and other objects float around in space because there is no gravity acting on them, as gravity is a force that primarily acts near the surface of the Earth.
What is the force that causes a bouncing ball to slow down and eventually stop?
-The force that causes a bouncing ball to slow down and eventually stop is called frictional force or friction, which acts in the opposite direction to the motion when two surfaces are in contact.
What is the role of friction when we walk?
-When we walk, friction acts between our shoes and the ground, providing the necessary grip to prevent slipping and falling. Without sufficient friction, we would not be able to walk properly.
What is the contact force that acts against motion when two surfaces are in contact?
-The contact force that acts against motion when two surfaces are in contact is called friction.
How can viewers get in touch with the creators of the video if they have queries?
-If viewers have any queries, they can write to the creators at studypod01@gmail.com.
Outlines
🧲 Introduction to Forces
This paragraph introduces the concept of different types of forces, such as magnetic, electric, gravity, and friction. It explains that a magnetic force can attract materials like iron and steel without contact and that magnets have two poles which can either attract or repel each other. An experiment is suggested to demonstrate electric force by rubbing a balloon on clothing to generate static electricity, attracting hair or small pieces of paper.
🌐 Gravity and Everyday Experiences
The paragraph delves into the concept of gravity, the force that pulls objects towards the center of the Earth, explaining why objects fall to the ground and why we always land after jumping. It contrasts this with the absence of gravity in space, which allows astronauts to float. The paragraph uses the example of a ball thrown in the air to illustrate the effect of gravity.
🏀 The Role of Friction
This section discusses friction, the force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact, causing a moving object like a bouncing ball to slow down and eventually stop. Friction is described as a contact force that acts in the opposite direction of motion. The importance of friction in everyday activities such as walking is highlighted, noting that without sufficient friction, we would slip and fall.
📚 Conclusion and Contact Information
The final paragraph wraps up the video by summarizing the forces discussed: magnetic, electric, gravity, and friction. It invites viewers with queries to reach out via email for further clarification, providing the address studypod01@gmail.com as the contact point.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Forces
💡Magnetic Force
💡Electric Force
💡Gravity
💡Friction
💡Non-Contact Force
💡Attraction
💡Repulsion
💡Electrically Charged
💡Experiment
💡Motion
Highlights
Introduction to different types of forces
Magnetic force can attract objects made of iron and steel
Magnetic force is a non-contact force acting without touching objects
Magnet poles: south and north poles attract each other, unlike poles repel
Experiment with a balloon and clothing to demonstrate electric force
Rubbing a balloon on clothes charges it and attracts hair or paper pieces
Electric force is the force between electric charges
Gravitational force or gravity pulls objects towards the Earth's center
Objects in the air fall back to the ground due to gravity
Absence of gravity in space allows astronauts to float
Frictional force or friction acts against motion when surfaces are in contact
Friction slows down and eventually stops a moving ball
Friction is necessary for walking; without it, we would slip and fall
Summary of forces discussed: magnetic, electric, gravity, and friction
Contact information provided for queries: studypod01@gmail.com
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: