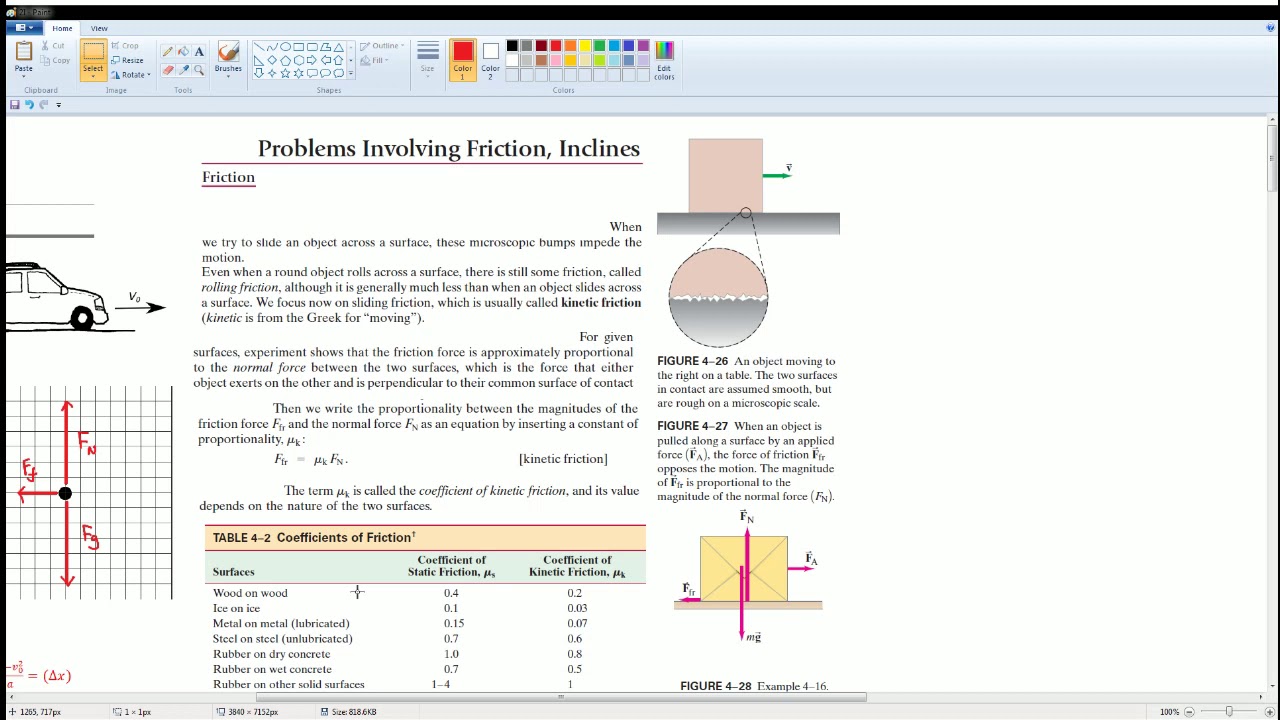
Slipping, Sliding Science! | Physics for Kids
TLDRThe video script explores the science behind the fun of a backyard water slide, focusing on the concept of friction. It explains that slipperiness occurs when two surfaces touch and slide against each other, and this is influenced by the amount of friction between them. A smooth plastic surface and water together create a slippery environment for the water slide. The script uses examples like a wet bar of soap and walking on ice to illustrate the effects of friction. It also encourages viewers to conduct their own experiments at home to understand friction better, such as walking on different surfaces or pushing a book across various materials. The video ends with an invitation for viewers to ask questions about any topic, including water slides, and to engage with the SciShow Kids community.
Takeaways
- 🎢 A backyard water slide is a fun summer activity that involves laying a plastic sheet on the lawn and spraying it with water.
- 💧 The slipperiness of a water slide is created by the interaction between the plastic, water, and the person sliding.
- 🤔 Slipperiness is experienced when two surfaces touch and rub against each other, which can either cause sliding or prevent it.
- 🛝 Friction is the force that opposes the sliding of two surfaces against each other and determines how easy it is to slide.
- 📚 The smoother the surface, the less friction there is, which makes it easier to slide, like the plastic slide compared to grass.
- 🚫 Without water, the slide would be too frictional to slide down, and without the plastic, the grass would not provide a slippery enough surface.
- 💧 Water acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the plastic slide and the person, allowing for smooth sliding.
- 🧦 Different materials and conditions affect friction; for example, socks on a smooth floor cause more sliding than sneakers.
- 🧪 At-home experiments can demonstrate friction by pushing a book across various surfaces like a table, a bath towel, or a metal baking sheet.
- 🤸♂️ The roughness of a surface, like a sidewalk compared to a tabletop, increases friction, making it harder to slide objects.
- ❄️ Ice is very slippery because it is smooth and creates less friction than dry pavement, which is why it's easier to slide on.
- 📧 SciShow Kids encourages viewers to ask questions and conduct their experiments to understand concepts like friction and slipperiness better.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a backyard water slide?
-The primary purpose of a backyard water slide is to provide a fun and engaging summertime activity where one can slide down the wet plastic surface for enjoyment.
What are the three essential components required to create a water slide?
-The three essential components required to create a water slide are a long piece of plastic, water, and a person to slide on it.
How does the concept of slipperiness relate to the experience of using a water slide?
-Slipperness is directly related to the experience of using a water slide as it is the reduced friction between the plastic surface and the person that allows for the sliding motion.
What is friction and how does it affect the sliding experience on different surfaces?
-Friction is a force that opposes the motion of two surfaces sliding against each other. A higher friction means more resistance to sliding, while lower friction allows for smoother and easier sliding.
Why does adding water to a plastic surface make it slippery?
-Adding water to a plastic surface makes it slippery because the water acts as a lubricant, reducing the friction between the plastic and the person sliding, thus allowing for easier movement.
What would happen if you tried to slide down a plastic surface without water?
-Without water, the plastic surface would have higher friction, making it difficult or even impossible to slide down because the lack of lubrication would cause the person to stick to the surface.
How does the smoothness of a surface contribute to its slipperiness?
-The smoothness of a surface contributes to its slipperiness by reducing the friction between the two sliding surfaces. A smoother surface offers less resistance, allowing objects or people to slide more easily.
Why is it easier to slide on a plastic surface than on grass?
-It is easier to slide on a plastic surface than on grass because plastic provides a smoother and more uniform surface, which reduces friction compared to the uneven and rough texture of grass.
What is an example of a situation where friction is beneficial and prevents slipping?
-An example where friction is beneficial is when walking on a sidewalk. The friction between the soles of your shoes and the sidewalk prevents you from slipping and allows for stable walking.
How can experimenting with different surfaces help us understand friction better?
-Experimenting with different surfaces can help us understand friction better by demonstrating how the texture, material, and smoothness of a surface can affect the ease or difficulty of sliding or moving an object across it.
What is the role of water in reducing friction on a water slide?
-The role of water in reducing friction on a water slide is to create a thin, slippery layer between the plastic surface and the person, which minimizes the contact and resistance, allowing for a smoother and faster slide.
Outlines
😀 Summer Fun with Water Slides
This paragraph introduces the topic of backyard water slides and poses the question of why they are so much fun. It explains the basic components needed for a water slide to work: a long piece of plastic, water, and the person sliding. The paragraph also touches on the concept of slipperiness and how it occurs when two things touch and rub against each other. Examples are given to illustrate slippery vs non-slippery surfaces, and the importance of friction in determining the slipperiness of a surface is discussed.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Backyard Water Slide
💡Slippery
💡Friction
💡Plastic
💡Water
💡Surface Roughness
💡Experimentation
💡Sneakers
💡Ice
💡Soap
💡Force
Highlights
Backyard water slides are a favorite summertime activity, providing fun by creating a slippery surface with a plastic sheet, water, and a person's body.
Slippery surfaces occur when two things touch and rub against each other, like a wet bar of soap against your hand.
Friction is the force that prevents sliding when two surfaces touch; more friction makes it harder for surfaces to move against each other.
The smoothness of a surface affects the amount of friction; rougher surfaces like sidewalks create more friction than smooth tabletops.
Walking on the sidewalk typically doesn't result in slipping due to the high friction between shoes and the pavement.
Icy surfaces are slippery because the smooth ice creates less friction compared to dry pavement, making it harder to walk without slipping.
Things are more slippery when there is less friction, which is key to the fun of a backyard water slide.
Without water, a plastic slide would not be滑 (slippery), emphasizing the importance of water in reducing friction.
The plastic slide provides a smoother surface than grass, contributing to the slipperiness of the water slide.
Water acts as a barrier between the plastic and the person's body, creating a slippery layer that allows for smooth sliding.
Home experiments can demonstrate friction by comparing the ease of sliding across different surfaces, such as wood floors versus socks on the same floor.
Experimenting with different surfaces, like pushing a book across a bath towel versus a metal baking sheet, can illustrate the effect of surface texture on friction.
The SciShow Kids channel encourages viewers to conduct their own experiments and share their findings, fostering a love for science and exploration.
The importance of safety is highlighted when suggesting home experiments, emphasizing the need for caution.
Questions about various topics, including waterslides, bikes, or flowers, are welcomed and viewers are encouraged to reach out via comments or email.
The SciShow Kids community is inclusive, inviting children and adults alike to learn and engage with scientific concepts in a fun and accessible manner.
The transcript concludes with an invitation to join the next session, fostering a sense of ongoing learning and community.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: