Kidney Pain? How to treat Kidney Stones? Causes and Symptoms
TLDRThe video script discusses the formation, symptoms, and treatment of kidney stones. Kidney stones are common, affecting one out of ten people, and are formed when certain chemicals in urine become concentrated and stick together. Factors contributing to stone formation include medical conditions, medications, and dehydration. Symptoms include severe pain, nausea, and blood in urine. Treatment varies based on stone size and location, with small stones often passing naturally with increased water intake and pain medication. Larger stones may require medical procedures such as lithotripsy or scopes. Preventative measures include drinking plenty of water, reducing salt intake, and avoiding excessive oxalate-rich foods. The video emphasizes the importance of seeking medical advice for severe symptoms and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to prevent recurrence.
Takeaways
- 🤕 Severe pain, nausea, and blood in urine are common symptoms when kidney stones block the urinary tube.
- 💧 Kidney stones form when certain chemicals in the urine become concentrated and start to stick together, often due to dehydration or increased salt or protein intake.
- 🔍 The most common type of kidney stone is calcium oxalate, but there are other types like uric acid and struvite.
- 📉 The risk of developing kidney stones increases with certain medical conditions, certain medications, and bacterial infections.
- 🚫 If a kidney stone is causing severe pain, uncontrollable nausea or vomiting, blood in the urine, fever, or difficulty passing urine, medical attention is necessary.
- 💊 Treatment for kidney stones depends on their size and location and can range from pain medication to procedures like lithotripsy or ureteroscopy.
- 💧 Drinking two to three liters of water daily can help prevent and assist in passing small kidney stones.
- 🧂 Reducing salt intake and moderating meat consumption can help prevent the formation of calcium oxalate stones.
- 🥦 Limiting foods high in oxalates, such as spinach and nuts, can also be beneficial for those prone to kidney stones.
- 🧊 Consuming diuretics or drinks with caffeine without adequate water intake can lead to dehydration, increasing the risk of kidney stones.
- 🙏 Maintaining good hydration and a balanced diet can help prevent kidney stones and promote overall health.
Q & A
What are some common symptoms of kidney stones when they block the urinary tube?
-Common symptoms include severe pain, nausea, and blood in the urine.
How often do people typically develop kidney stones?
-Kidney stones are common, with one out of every ten people developing a kidney stone at some point in their life.
What is the role of kidneys in the body?
-Kidneys are responsible for cleaning the blood and removing waste material into the urine, processing about five liters of blood nearly 400 times every day.
What factors can contribute to the formation of kidney stones?
-Factors include certain medical conditions, medications, bacterial infections, and an imbalance of chemicals in the urine. Additionally, a diet high in salt or protein and low water intake can increase the risk.
What are the different types of kidney stones?
-Kidney stones are made of different chemicals; the most common type is calcium oxalate, while others can be made of uric acid, struvite, or other materials.
When should someone seek medical attention for kidney stones?
-One should seek medical attention if experiencing severe pain, uncontrollable nausea or vomiting, blood in the urine, fever, difficulty passing urine, or if they have silent kidney stones that may damage the kidneys over time.
How can kidney stones be treated if they are small and not causing blockage?
-Small stones may pass without procedures. Drinking two to three liters of water daily helps dilute the urine, and pain medicines can ease the pain. Medicines that relax the ureter or dissolve the stone may also be prescribed.
What are some medical procedures used for treating larger kidney stones?
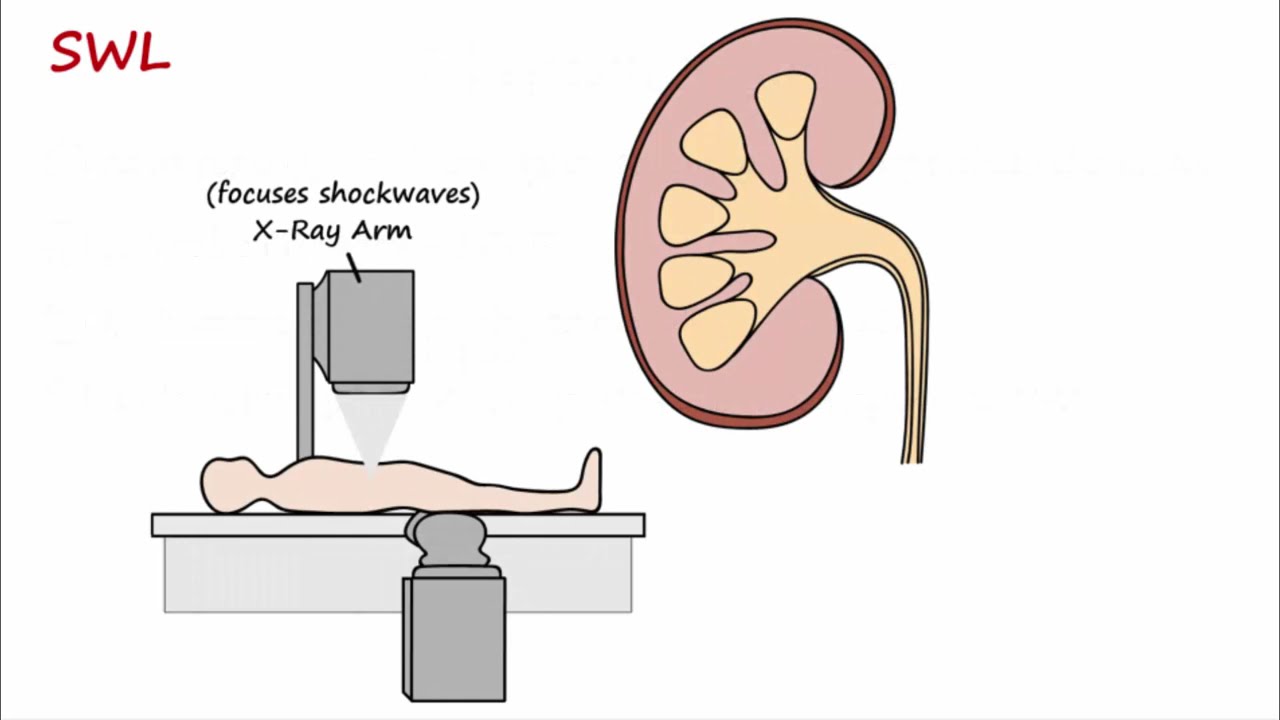
-For large stones, procedures may include shock wave lithotripsy, which uses shock waves to break the stones, or using a scope to break and remove the stones from the ureter or kidney. In some cases, a small tube may be inserted into the kidney to remove the stone.
How can diet changes help prevent further kidney stone formation?
-Drinking plenty of water, reducing salt intake, moderating meat consumption, and limiting foods high in oxalates can help prevent further stone formation.
Why is it important to stay hydrated and what is the recommended daily water intake to prevent kidney stones?
-Staying hydrated helps keep urine dilute, reducing the chance of stone formation. It is recommended to drink at least three to four liters of water every day, with more on hot days.
What is the relationship between diuretics, caffeine, and kidney stones?
-Diuretics and drinks with caffeine can make a person urinate more, which can lead to dehydration if not accompanied by sufficient water intake, potentially contributing to kidney stone formation.
Why should one consult a doctor if they develop stones repeatedly?
-Recurrent kidney stones may indicate an underlying cause that needs medical attention. Consulting a doctor can help identify and address the root cause to prevent future occurrences.
Outlines
😖 Understanding Kidney Stones
This paragraph discusses the formation, symptoms, and treatment of kidney stones. Kidney stones are common, affecting one out of ten people, and can form when certain chemicals in urine become concentrated. They can be caused by medical conditions, medications, bacteria, or be of unknown origin. Symptoms include severe pain, nausea, and blood in urine, which can be indicative of a blockage in the urinary tube. Treatment varies based on the stone's size and location and may include increased water intake, pain medication, and medical procedures like lithotripsy or ureteroscopy. The paragraph also emphasizes the importance of seeking medical attention if experiencing severe symptoms or if stones are recurring.
🍽️ Preventing Kidney Stones Through Diet
The second paragraph focuses on dietary changes to prevent kidney stones. It highlights the importance of hydration, recommending at least three to four liters of water daily, especially on hot days. Reducing salt intake and moderating meat consumption are also advised to decrease the risk of stone formation. The paragraph suggests avoiding foods high in oxalates, which contribute to the most common type of kidney stone, calcium oxalate. It clarifies that consuming calcium-rich foods does not typically cause problems with stones, but advises consulting a doctor before taking calcium supplements. Lastly, it encourages seeking medical advice for recurrent stones to identify underlying causes.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Kidney stones
💡Ureters
💡Urine concentration
💡Calcium oxalate
💡Dehydration
💡Pain management
💡Lithotripsy
💡Diet restrictions
💡Medical conditions
💡Infections
💡Diuretics
Highlights
Kidney stones are common, affecting one out of 10 people at some point in their life.
Kidney stones can form when certain chemicals in the urine become too concentrated due to less water intake.
Medical conditions like gout, hormone imbalance, or inflammatory bowel disease can cause kidney stones.
Certain medications, bacteria, and infections can also trigger stone formation.
Dehydration increases the risk of kidney stones by concentrating the urine.
The most common type of kidney stone is calcium oxalate.
Symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain, nausea, and blood in urine.
Smaller stones (less than half a centimeter) may pass on their own.
Seek medical attention for severe pain, uncontrollable nausea, blood in urine, fever, or difficulty passing urine.
Treatment options for kidney stones include ultrasound, CT scan, blood and urine tests, and various medical procedures.
Drinking two to three liters of water daily can help prevent kidney stones.
Medications can be prescribed to help relax the ureter and dissolve the stone.
Shock wave lithotripsy is a treatment that uses shock waves to break stones into smaller pieces.
For larger stones, a scope may be used to break and remove them from the ureter or kidney.
Diet changes, such as drinking more water and reducing salt intake, can help prevent recurrent kidney stones.
Limiting foods high in oxalates and moderating meat consumption can also reduce the risk of kidney stones.
Diuretics and drinks with caffeine can increase urination but may lead to dehydration if not balanced with water intake.
Consult a doctor to find the underlying cause if you develop stones repeatedly.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

What causes kidney stones? - Arash Shadman
Kidney Stones - Types, Formation, Treatment, Prevention

Everything You Need to Know About Urinary Stones | Caroline Wallner, MD | UCLAMDChat

Urine Crystals & Kidney Stones

Kidney Stones (Renal Calculi) Nursing Lecture Symptoms, Treatment, Causes NCLEX

Medical Animation: Kidney Stone Disease
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: