What causes kidney stones? - Arash Shadman
TLDRThe video script discusses kidney stones, which are hard crystalline masses that form in the urinary tract. The largest recorded stone weighed over a kilogram and was as large as a coconut. These stones are made of compounds like calcium, sodium, and uric acid, which can crystallize if urine levels are too high or too acidic/basic. Calcium oxalate is the most common crystal, forming about 80% of stones. Symptoms include severe pain, blood in urine, nausea, and vomiting. Most stones less than five millimeters pass naturally, while larger ones may require medication, soundwave lithotripsy, or surgery. Prevention includes drinking water, limiting high-oxalate foods, and ensuring adequate calcium intake. Despite increasing rates, the record for the largest kidney stone is unlikely to be broken soon.
Takeaways
- 📏 The largest recorded kidney stone weighed over a kilogram and was 17 centimeters in diameter.
- 🌿 Kidney stones form inside the body from compounds in urine such as calcium, sodium, potassium, oxalate, uric acid, and phosphate.
- 🔬 If urine becomes too acidic or basic, these particles can crystallize and form stones over time.
- 💠 Calcium oxalate is the most common crystal in kidney stones, accounting for about 80%.
- 🦠 Certain kidney stones can be caused by bacterial infections or result from genetic disorders or medication.
- 🚑 Kidney stones often go unnoticed until they move, causing severe pain and sometimes blood in urine.
- 💊 Small kidney stones (less than 5mm) can usually pass naturally with increased water intake and possibly painkillers.
- 💊 For slightly larger stones, medications like alpha blockers can help, and potassium citrate can make urine less acidic to dissolve the stones.
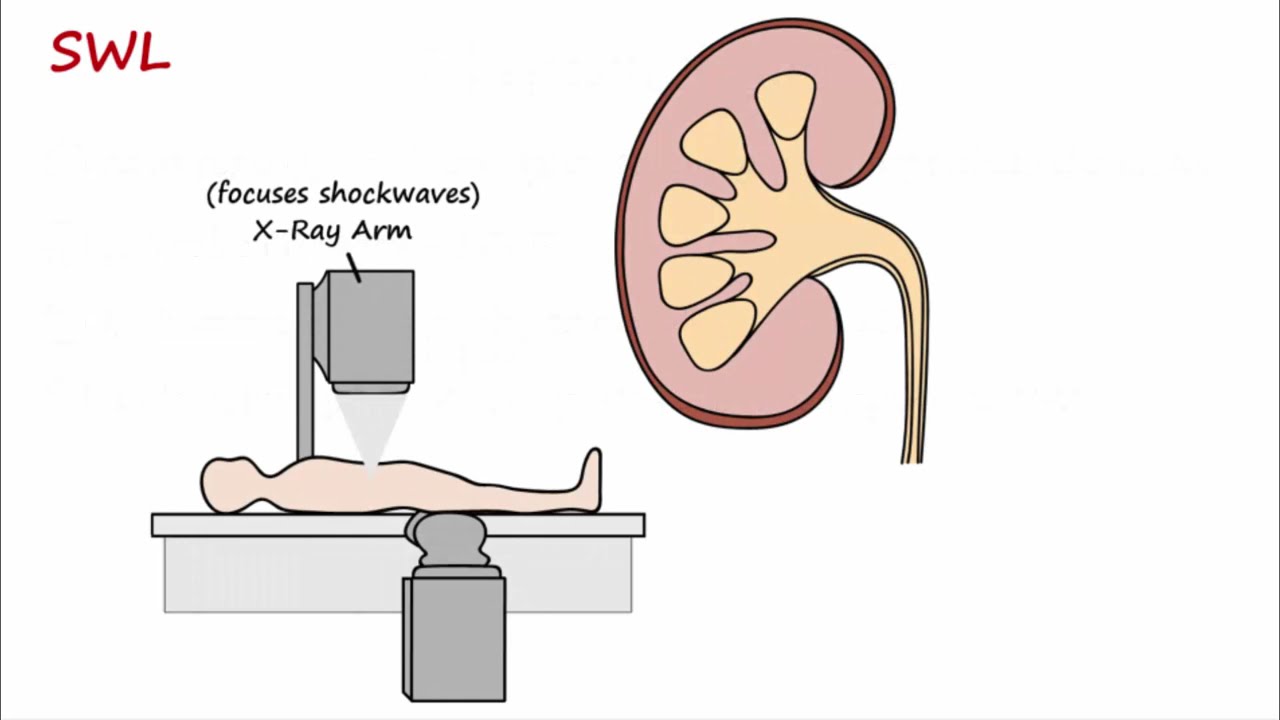
- 📍 Medium-sized stones can be treated with extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, which uses sound waves to break the stone into smaller pieces.
- 🔧 Larger stones may require more invasive treatments, such as stents, laser pulses, or surgical removal.
- 🥤 To prevent kidney stones, doctors recommend drinking plenty of water, limiting high-oxalate foods, and ensuring adequate calcium intake.
Q & A
What is the weight and diameter of the biggest kidney stone on record?
-The biggest kidney stone on record weighed more than a kilogram and was 17 centimeters in diameter.
Where do kidney stones form and what are they made of?
-Kidney stones form inside the body and are hard masses of crystals that can form in the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra.
What are the common compounds found in urine that can contribute to the formation of kidney stones?
-Urine contains compounds such as calcium, sodium, potassium, oxalate, uric acid, and phosphate.
What happens when the levels of certain particles in urine get too high or urine becomes too acidic or basic?
-If the levels of these particles get too high, or if urine becomes too acidic or basic, the particles can clump together and crystallize, potentially forming a kidney stone.
What is the most common type of crystal that forms kidney stones?
-Calcium oxalate is the most common type of crystal to form kidney stones, accounting for about 80% of cases.
What are some less common materials that kidney stones can be made of?
-Less common kidney stones are made of calcium phosphate or uric acid.
How can a kidney stone cause pain when it moves?
-When a stone travels through the kidney and into the ureter, its sharp edges scratch the walls of the urinary tract, and nerve endings in this tissue transmit excruciating pain signals through the nervous system.
What are the symptoms that can accompany a kidney stone?
-Symptoms of a kidney stone can include nausea, vomiting, and a burning sensation while urinating.
What happens if a kidney stone is large enough to block the flow of urine?
-If a stone is large enough to block the flow of urine, it can create an infection, cause backflow, and potentially damage the kidneys themselves.
What is the typical treatment for smaller kidney stones that are less than five millimeters in diameter?
-For stones less than five millimeters in diameter, a doctor will often recommend drinking large amounts of water to help the stone pass and may also prescribe painkillers.
How does extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy help in treating medium-sized kidney stones?
-Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy uses high-intensity pulses of focused ultrasonic energy aimed directly at the stone, creating vibrations and small bubbles that crush the stone into smaller pieces, making it easier to pass out of the body.
What are some preventive measures for avoiding kidney stones?
-Preventive measures include drinking plenty of water to dilute calcium oxalate and other compounds, limiting foods high in oxalate such as potato chips, spinach, rhubarb, and beets, and ensuring adequate calcium intake, as it can bind to oxalate in the digestive tract before it reaches the kidneys.
Outlines
😱 The Largest Kidney Stone Ever Recorded
The script discusses the largest kidney stone ever documented, which was over a kilogram in weight and 17 centimeters in diameter. It clarifies that kidney stones form internally and can be extremely painful to pass. These stones are composed of crystallized compounds found in urine, such as calcium, sodium, potassium, oxalate, uric acid, and phosphate. When the concentration of these compounds is too high or urine pH is off, they can form crystals that grow into stones over time. Calcium oxalate is the most common crystal type in kidney stones, making up about 80% of cases. Other types include calcium phosphate and uric acid stones, while struvite stones are less common and often caused by bacterial infections. Genetic disorders and certain medications can also lead to rarer types of kidney stones. The symptoms of kidney stones typically arise when they move, causing pain and sometimes blood in urine. If large enough to obstruct urine flow, they can lead to infection or kidney damage. However, smaller stones often pass without issue, sometimes aided by increased water intake and painkillers. Larger stones may require medication to help with passage, while medium-sized stones may be treated with extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, which uses sound waves to break the stone into smaller pieces. Invasive procedures are sometimes necessary for very large stones. The script concludes with advice on how to prevent kidney stones, including hydration, dietary recommendations, and the potential benefits of calcium intake. It also notes that kidney stone rates are increasing, though it's unlikely the record for the largest stone will be surpassed soon.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Kidney Stone
💡Calcium Oxalate
💡Uric Acid
💡Struvite
💡Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
💡Stent
💡Laser Lithotripsy
💡Potassium Citrate
💡
💡Nausea and Vomiting
💡Hydration
💡Genetic Disorders
💡Diet and Lifestyle
Highlights
The largest recorded kidney stone weighed over a kilogram and was 17 centimeters in diameter.
Kidney stones form inside the body and can be extremely painful to pass.
They are hard masses of crystals that can form in various parts of the urinary system.
Urine contains compounds like calcium, sodium, potassium, oxalate, uric acid, and phosphate.
High levels of these particles or imbalanced urine pH can lead to crystallization and stone formation.
Calcium oxalate is the most common crystal type in kidney stones, accounting for about 80%.
Less common types include calcium phosphate and uric acid stones.
Struvite stones are caused by bacterial infections, while rarer stones can result from genetic disorders or medications.
Kidney stones often go undetected until they move and cause pain.
As stones move, they can scratch urinary tract walls and cause blood in urine, nausea, vomiting, and burning sensations.
Large stones can block urine flow, leading to infections and kidney damage.
Most kidney stones are not serious and do not require invasive treatment.
Small stones (less than 5mm) usually pass out of the body on their own.
Drinking water and taking painkillers can help with passing small stones.
Medications like alpha blockers and potassium citrate can assist with stone passage and dissolution.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy uses sound waves to break down medium-sized stones.
Invasive treatments like stents, laser pulses, and surgery are used for larger stones.
To prevent kidney stones, it's recommended to drink plenty of water and limit high-oxalate foods.
Calcium in the diet can help bind oxalate and prevent stone formation.
Kidney stone rates are rising, but the world record for the largest stone is unlikely to be broken soon.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Medical Animation: Kidney Stone Disease

Kidney Pain? How to treat Kidney Stones? Causes and Symptoms

Urinary Alkalinization for Kidney Stones

Urine Crystals & Kidney Stones
Kidney Stones - Types, Formation, Treatment, Prevention

Eliminate Kidney Stones With Lemons – Kidney Stone Causes & Lemon Benefits – Dr.Berg
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: