Renal System 1, Urinary system and kidneys
TLDRThe video script introduces the urinary system, emphasizing its main components. It highlights the presence of two kidneys, with the right kidney positioned slightly lower due to the liver's influence. The kidneys' connection to the ureters, which are the ducts that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder, is also discussed. The ureters' path through the abdominal cavity is briefly mentioned, providing a foundational understanding of the urinary system's structure and function.
Takeaways
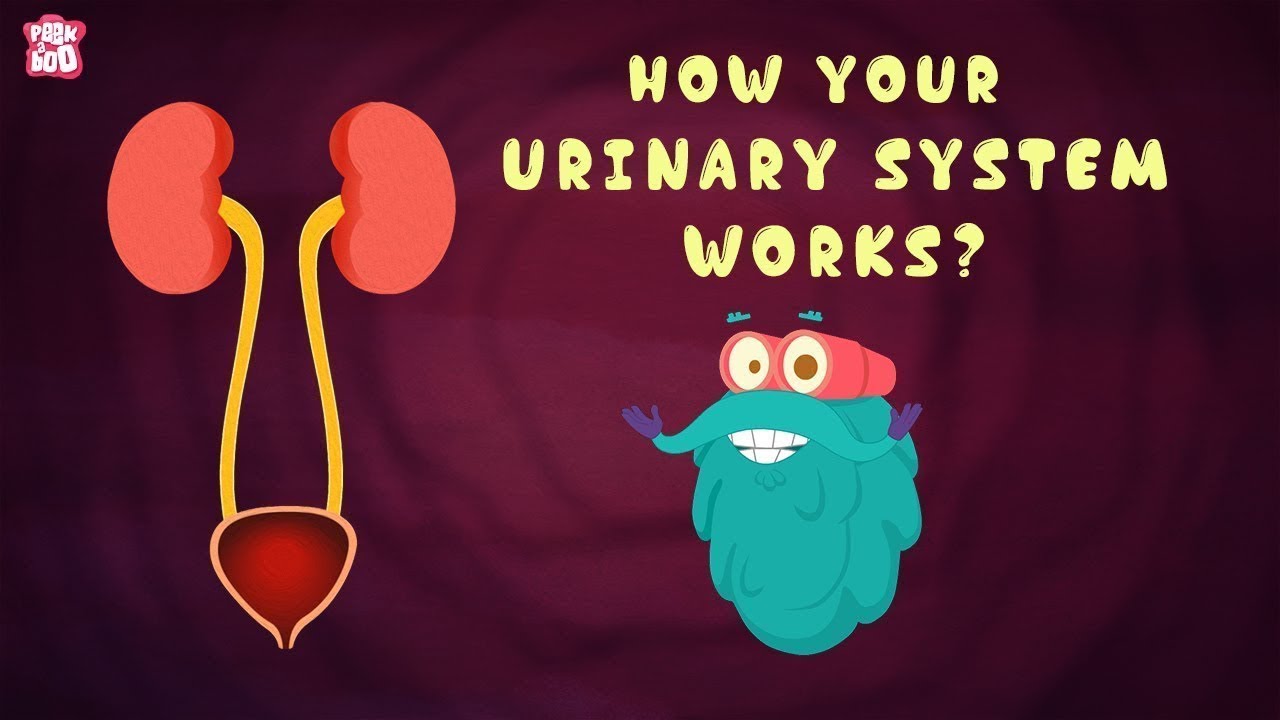
- 🧘 The urinary system is composed of two main kidneys, the right and the left.
- 🔄 The right kidney is positioned slightly lower than the left due to the liver being located above it.
- 💧 Kidneys are responsible for filtering blood and producing urine, which passes through the ureters.
- 🚰 Ureters are ducts that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- 📍 The ureters travel posteriorly down to the abdominal cavity.
- 🤔 The script contains a series of repeated phrases and unrelated characters which seem to be errors or placeholders rather than key information.
- 🧬 The anatomical position of the kidneys and their connection to the ureters is crucial for the urinary system's function.
- 🧊 The liver's position affects the positioning of the right kidney, illustrating the interplay between different organs.
- 🔗 The urinary system's components work together to maintain the body's fluid balance and remove waste products.
- 🛡️ The kidneys play a vital role in filtering toxins and excess substances from the blood.
- 💊 The script's mention of the liver's influence on kidney position underscores the importance of organ relationships in overall body function.
- 📝 The presence of nonsensical text in the script suggests the need for careful review and editing to ensure accurate information is conveyed.
Q & A
What are the main components of the urinary system?
-The main components of the urinary system include two kidneys, ureters, and a bladder. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce urine, which then travels down the ureters to the bladder for storage before being expelled from the body.
How many kidneys does the human body have and what is their anatomical position?
-The human body has two kidneys, the right kidney and the left kidney. The right kidney is positioned slightly lower than the left kidney due to the liver being located above it, which pushes it down.
What is the role of the liver in the positioning of the right kidney?
-The liver is located above the right kidney and is heavier, which effectively pushes the right kidney into a slightly lower position compared to the left kidney.
What is the function of the ureters in the urinary system?
-The ureters are ducts that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. They travel down to the abdominal cavity, allowing the urine to be stored before it is excreted.
Why are the kidneys connected to the ureters?
-The kidneys are connected to the ureters to facilitate the passage of urine from the kidneys to the bladder. This connection is essential for the elimination of waste products from the body.
What is the direction in which the ureters travel to reach the bladder?
-The ureters travel down (posteriorly) to the abdominal cavity to reach the bladder, where urine is stored before being excreted.
How does the urinary system contribute to maintaining homeostasis in the body?
-The urinary system plays a critical role in maintaining homeostasis by filtering waste products from the blood, regulating water balance, and controlling the levels of electrolytes, which are essential for the body's proper functioning.
What are some common issues that can affect the urinary system?
-Common issues that can affect the urinary system include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, kidney failure, and bladder infections. These conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the urinary system and may require medical intervention.
How does the bladder store urine before it is expelled from the body?
-The bladder is a muscular sac that expands as it fills with urine. It stores the urine until the body is ready to expel it through the process of urination, during which the bladder muscles contract and the urine is released through the urethra.
What is the significance of the kidneys' position in the body?
-The kidneys' position, located towards the back of the abdominal cavity, provides them with protection from external damage due to their encasement by the lower rib cage. Additionally, their position allows for efficient filtration of blood and the production of urine.
How does the liver's position above the right kidney impact its function?
-The liver's position above the right kidney does not significantly impact the kidney's function. However, it does result in the right kidney being slightly lower than the left, which is a normal anatomical variation.
What is the process of urine formation in the kidneys?
-Urine formation in the kidneys involves a process called nephron filtration, where blood is filtered through tiny units called nephrons. This process removes waste products, excess water, and electrolytes to form urine, which is then passed into the renal pelvis and collected by the ureters for transport to the bladder.
Outlines
🧘 Anatomy and Function of the Urinary System
The video begins with an introduction to the urinary system, focusing on its main components. It emphasizes the presence of two kidneys, the right and left, with the right kidney positioned slightly lower due to the liver's location above it. The kidneys' connection to the ureters, which are the ducts that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, is also mentioned. The ureters are described as traveling posteriorly into the abdominal cavity. The paragraph, however, contains several repetitions and appears to have some corrupted text, which makes it challenging to extract further meaningful information.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Urinary System
💡Kidneys
💡Ureters
💡Bladder
💡Liver
💡Anatomical Position
💡Peristaltic Contractions
💡Abdominal Cavity
💡Urine
💡Posteriorly
Highlights
The main components of the urinary system are the two kidneys.
The right kidney is anatomically positioned slightly lower than the left kidney due to the liver located above it.
Kidneys are connected to ureters, which are the ducts through which urine passes from the kidney to the bladder.
Ureters travel down posteriorly to the abdominal cavity.
The urinary system plays a crucial role in filtering waste and excess substances from the blood to form urine.
The kidneys are responsible for maintaining the body's electrolyte balance and regulating blood pressure.
The kidneys also produce hormones that help regulate red blood cell production and calcium metabolism.
The bladder stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body through the urethra.
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The urinary system works in conjunction with the circulatory system to maintain overall body homeostasis.
Kidney stones or urinary tract infections can cause significant problems within the urinary system.
Diuretics can be used to increase urine production and help flush out excess fluids and toxins from the body.
Adequate hydration is essential for the proper functioning of the urinary system.
The urinary system plays a key role in maintaining the body's acid-base balance.
Prolonged dehydration can lead to urinary system problems such as kidney failure.
The urinary system is susceptible to various diseases and disorders, including urinary incontinence and interstitial cystitis.
Regular check-ups and screenings can help detect and prevent urinary system problems early on.
A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can contribute to a healthy urinary system.
Advancements in medical technology have led to improved treatments and surgical procedures for urinary system disorders.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Kidneys (Functions, Structures, Coverings, Nephron) - Urinary System Anatomy

The Urinary System In 7 Minutes

How is urine produced in the body?KIDNEY, NEPHRON, BLADDER FUNCTION|Anatomy of the Urinary System

Urinary/Kidney Stones - Overview (signs and symptoms, risk factors, pathophysiology, treatment)
How Your Urinary System Works? - The Dr. Binocs Show | Best Learning Videos For Kids | Peekaboo Kidz

What If You Hold Your Urine For Too Long? | How Urinary System Works? | The Dr Binocs Show For Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: