Objects
TLDRIn this insightful AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explores the concept of objects versus systems, using the kilogram as a tangible example and contrasting it with the microscopic complexity of objects at an atomic level. He delves into how the scale of observation influences whether something is considered an object or a system, and illustrates this with the macroscopic study of planetary orbits versus the microscopic examination of salt and sugar in a solution, highlighting the importance of understanding both the macroscopic and microscopic perspectives depending on the scientific question at hand.
Takeaways
- 📈 The kilogram is the only SI unit based on a physical object, stored in Paris, which presents challenges for precise measurements.
- 🔍 The Avogadro Project aims to redefine the kilogram based on Avogadro's Number, using a highly spherical object with minimal variation when scaled up.
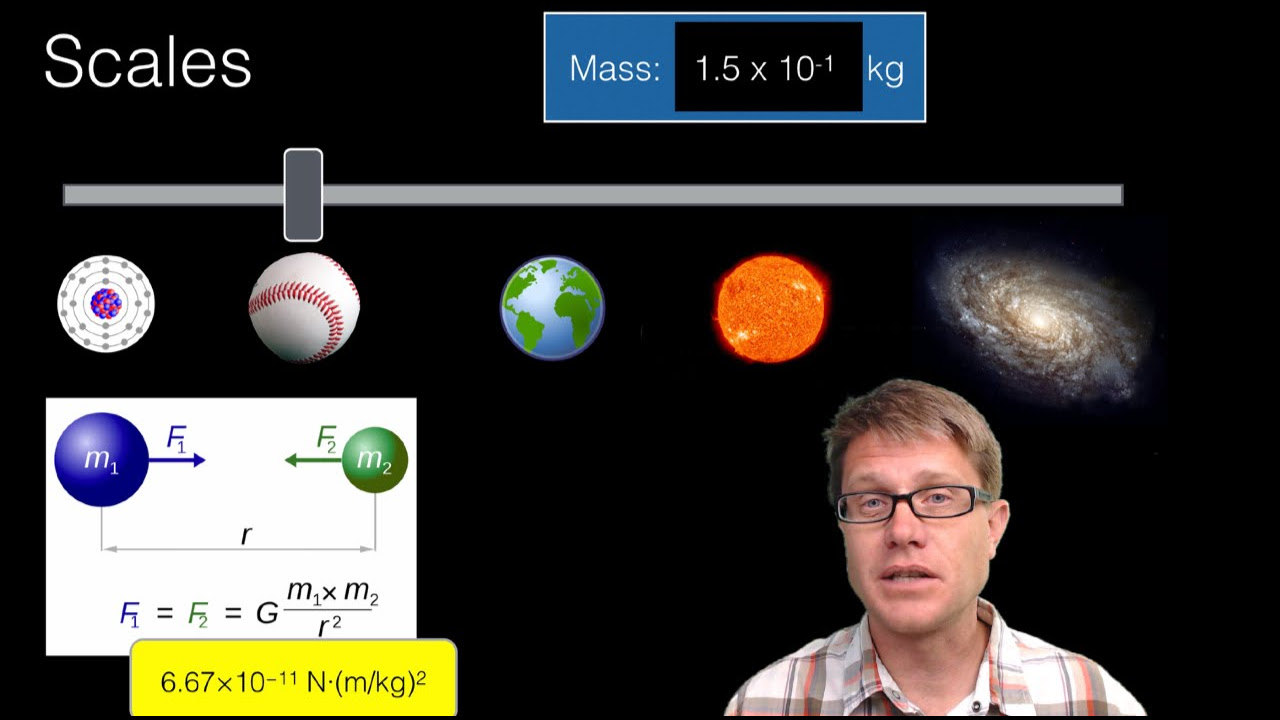
- 🎓 An object can be considered as a single entity in macroscopic studies, but as a system when examining its microscopic components and interactions.
- 🔬 Systems are collections of objects interconnected in some way, and the study of them can vary depending on the level of detail required.
- 🌍 When studying celestial bodies like planets, treating them as objects is sufficient for understanding their orbits without needing to consider their composition.
- 🧪 In a science lab, understanding the differences between substances like salt and sugar at a microscopic level requires treating them as systems, not just objects.
- 💧 Adding salt to water increases concentration, which can be visually represented in a simulation, and affects the conductivity of the solution.
- 🍬 Similarly, adding sugar to water also increases concentration, but the rate and effects on conductivity differ from those of salt.
- 🔋 Introducing a battery into a saltwater solution can demonstrate conductivity, which is a property not shared by a sugar solution.
- 🤔 The approach to modeling a system's properties depends on the specific question being asked and the desired level of understanding.
- 🎯 Determining a system's properties involves understanding how its constituent parts interact and contribute to its overall behavior.
Q & A
What is the significance of the kilogram as described in the video?
-The kilogram is significant because it is the only unit based on the mass of a physical artifact stored in Paris, making it somewhat problematic due to potential variations in its mass.
What is the Avogadro Project attempting to achieve?
-The Avogadro Project is working to redefine the kilogram based on Avogadro's Number, aiming to create a more consistent and reliable standard for mass measurement.
How is the most spherical object created by the Avogadro Project described in the video?
-The most spherical object created by the Avogadro Project is so perfectly spherical that if it were blown up to the size of the Earth, there would be no more variation than 2.5 meters around the whole object.
What is the difference between an object and a system in the context of physics?
-An object is a single, discrete entity, while a system is a collection of objects that are connected or interact with each other in some way. The choice between treating something as an object or a system depends on the scale and the specific question being addressed.
Why is it important to understand both the macroscopic and microscopic perspectives when studying physical phenomena?
-Understanding both perspectives allows for a more comprehensive analysis of physical phenomena. The microscopic perspective can reveal details about atomic and molecular interactions that are not apparent when studying at a macroscopic level.
How does the macroscopic study of planets orbiting the sun differ from a microscopic study?
-In macroscopic study, planets can be treated as discrete objects without considering their molecular makeup, which simplifies the analysis of their orbits. Microscopic study would involve understanding the composition and interactions of the molecules within the planets.
What happens to the concentration when salt is added to water in the phet simulation?
-As salt is added to water, the concentration increases. Adding water decreases the concentration, while evaporating water increases it again. However, removing some of the solution does not change the concentration.
What is the observable difference in conductivity between salt and sugar solutions?
-When a battery is added to a salt solution, it lights up, indicating conductivity. However, a sugar solution does not light up, showing that it does not conduct electricity as effectively as salt.
What is the importance of understanding the substructure of a system to model its properties?
-Understanding the substructure is crucial because the properties of a system are determined by the interactions of its constituent parts. This knowledge allows for accurate modeling and prediction of system behavior.
How does the approach to studying a substance change depending on the level of detail required?
-The approach changes based on whether a macroscopic or microscopic perspective is needed. For a detailed understanding, such as the difference between salt and sugar at a molecular level, the substance must be treated as a system with interacting constituents.
What is the main takeaway from the video regarding the study of physical systems?
-The main takeaway is that the depth of analysis depends on the problem being addressed. It's essential to determine whether a macroscopic or microscopic approach is appropriate for understanding and modeling the properties of a system.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Objects and Systems in Physics
This paragraph introduces the concept of an object in the context of physics, specifically focusing on the kilogram as an example. It highlights the unique nature of the kilogram as the only unit based on a physical artifact, stored in Paris, and the challenges associated with this. The Avogadro Project's efforts to redefine the kilogram based on Avogadro's Number and the creation of a highly spherical object to define a unit are discussed. The distinction between an object and a system is explored, emphasizing the importance of understanding interactions and properties at a microscopic level for a system, but treating it as a single entity when studying macroscopic properties.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Avogadro Project
💡kilogram
💡object
💡system
💡macroscopic
💡microscopic
💡Avogadro's Number
💡Atwood machine
💡concentration
💡conductivity
💡sodium chloride
Highlights
The kilogram is the only unit based on the mass of an artifact.
The Avogadro Project aims to redefine the kilogram based on Avogadro's Number.
A highly spherical object has been created for the purpose of redefining the kilogram.
The spherical object's uniformity is such that if scaled to the size of the Earth, the variation would not exceed 2.5 meters.
Understanding the difference between an object and a system is crucial in physics.
Macroscopic study treats objects as discrete units regardless of their internal composition.
An Atwood machine is an example of a system composed of multiple objects.
The study of an object's composition becomes important when its make-up is relevant to the question at hand.
The scale of study determines whether an entity should be considered an object or a system.
Planetary orbits can be modeled as objects for simplicity in astronomical calculations.
The difference between salt and sugar becomes apparent when studied at a molecular level.
PhET simulations can illustrate the differences in molecular behavior between substances like salt and sugar.
Concentration and conductivity are properties that can be used to distinguish between salt and sugar solutions.
Understanding the properties of a system requires examining the interactions of its constituent parts.
The approach to modeling a system is dictated by the specific problem being addressed.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: