Physicist Breaks Down Superhero Physics From Movies & TV | WIRED
TLDRIn this engaging video script, physics professor Rhett Allain dissects the physics behind superhero feats in films. He explores the impracticality of superhero landings, the concept of kinetic energy as depicted in 'Black Panther', and the principles of recoil with 'Wonder Woman'. Allain also addresses the unrealistic aspects of Superman's strength and the terminal velocity of 'Captain America'. With a blend of humor and science, he highlights the fun in the fantastical physics of our favorite superheroes, reminding us that while these may not be scientifically accurate, they certainly make for great cinema.
Takeaways
- 🦸♂️ The 'superhero landing' with one knee, one fist, and a foot on the ground is a dramatic but impractical move that would be hard on the knees and not recommended for real-life landings.
- 🛡️ Black Panther's suit is depicted as capable of storing kinetic energy from bullets in an internal battery and releasing it later, showcasing the concept of kinetic energy in action.
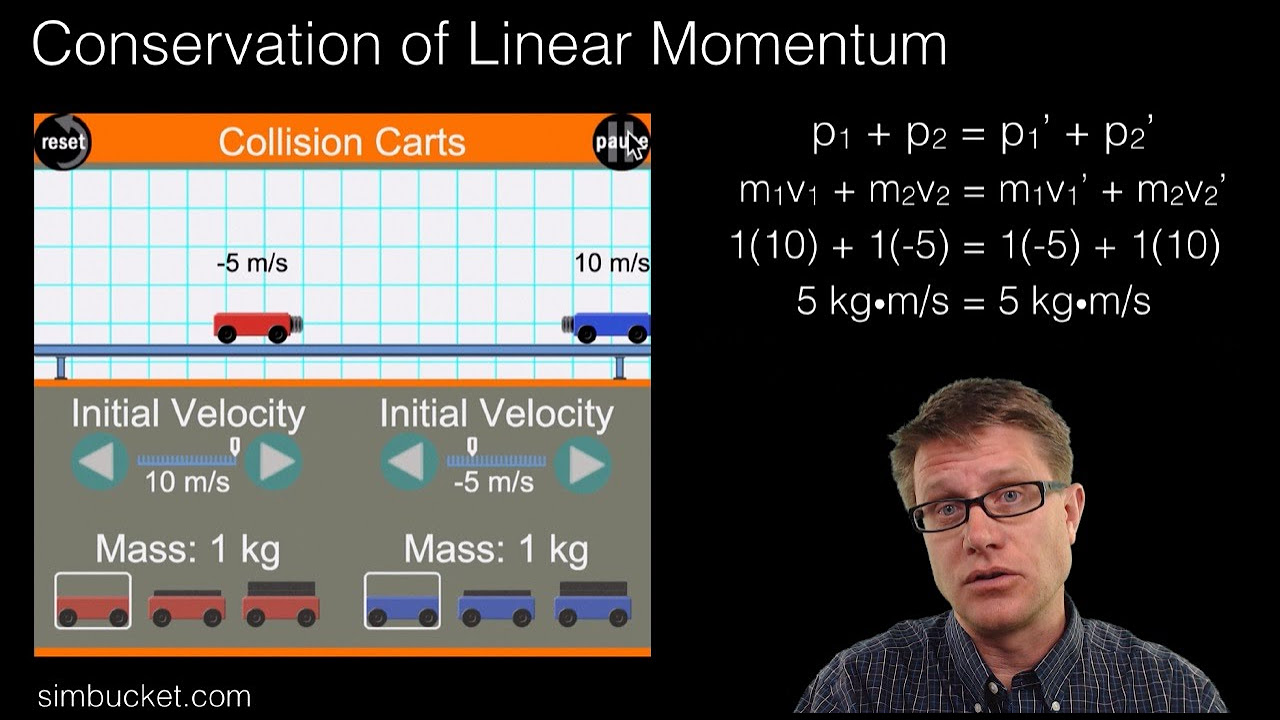
- 🔫 Recoil, as seen with Wonder Woman deflecting bullets, is explained by the conservation of momentum, where the force exerted on the bullet is met with an equal and opposite force on the person.
- 🏢 Superman's attempt to lift a building by pushing from the middle is deemed impossible due to the structural integrity of the building and the physics of force distribution.
- 🕸 Spider-Man's web's tensile strength is discussed in the context of his failure to keep a boat from breaking apart, highlighting the importance of force and material properties.
- 🛬 Captain America's terminal velocity and the physics of falling are explained, demonstrating how air resistance affects the speed at which a falling object reaches a constant velocity.
- 🤜 The concept of net force is explored through Iron Man's strategy to prevent a chain of people from falling by using electricity to force a grip, though it's pointed out as impractical.
- 💥 A-Train's high-speed collision in 'The Boys' is analyzed, questioning the physics of his invulnerability and the impact on a normal human.
- 🏃♂️ Running on water, as seen in 'The Incredibles', is humorously dismissed as requiring an impossibly fast and forceful interaction with the water's surface.
- 🚀 Iron Man's flight stability is attributed to the placement of thrusters in his hands, illustrating the importance of center of mass and thrust distribution in flight.
- 💪 The impact force and protection provided by Groot's rigid form in 'Guardians of the Galaxy' are discussed, emphasizing the role of structural flexibility and strength in crash protection.
Q & A
What is the superhero landing described in the video?
-The superhero landing is a dramatic pose where a superhero lands with one knee, one fist, and a foot on the ground, creating three contact points. It's a sudden and visually appealing move, but it's not practical for real-life landings as it can be hard on the knees.
Why is the superhero landing considered impractical?
-The superhero landing is impractical because it involves a sudden stop with minimal contact points, which can result in a large force acting on the body, potentially causing injury, especially to the knees.
What is a more effective way to land from a fall according to the video?
-A more effective way to land from a fall is to increase the distance over which you stop, such as bending the knees upon landing or performing a parachute landing fall, where you hit the ground and roll over to further increase the stopping distance and reduce the force of impact.
How does Black Panther's suit utilize kinetic energy?
-Black Panther's suit has the ability to interact with the kinetic energy of bullets, storing it in an internal battery. Once enough energy is stored, it can be released in an energy bolt for various uses, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood.
What is recoil and how does it relate to Wonder Woman deflecting a bullet?
-Recoil is the reaction force that occurs when an object is propelled in one direction, causing the source of the force to move in the opposite direction. In the case of Wonder Woman deflecting a bullet, the recoil would be minimal due to the bullet's low mass and high velocity, resulting in a small change in momentum for Wonder Woman.
Why would Superman's attempt to lift a building by pushing from the middle be ineffective?
-Superman's attempt would be ineffective because the building would likely collapse under the pressure. Pushing from the middle would cause the structure to bend or break, and the building's integrity would be compromised, leading to failure.
What is terminal velocity and how does Captain America achieve it?
-Terminal velocity is the constant speed reached during free fall when the air resistance force equals the gravitational force acting on the body, resulting in no net force and thus no acceleration. Captain America achieves terminal velocity by adjusting his body position to maximize air resistance, and then changing to a more vertical position to increase his falling speed.
How does the Iron Man suit stabilize flight?
-The Iron Man suit stabilizes flight by configuring thrusters in a way that allows for proper weight distribution and control. Having thrusters higher up and further apart from the body center of mass increases stability, similar to how real rockets use gimbals to change thrust direction.
What is the concept of forces coming in pairs as mentioned in the video?
-The concept of forces coming in pairs, also known as Newton's third law of motion, states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that any force exerted by one object onto another is met with an equal force in the opposite direction by the second object.
How does the video explain the impracticality of running on water?
-The video explains that running on water would require a continuous and forceful impact with the water to generate an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity. This would be extremely difficult and fast-paced, making it an impractical feat for a normal person.
What is the significance of the windup in Captain America's hammer swing in Avengers Endgame?
-The windup in Captain America's hammer swing increases the hammer's speed relative to his hand, resulting in a greater impact force when it connects with the target. This technique not only maximizes the force of the strike but also adds a visually impressive element to the action.
Outlines
🦸♂️ Superhero Physics: Landings and Kinetic Energy
Rhett Allain, a physics professor, explores the physics behind superhero feats in movies. He discusses the impracticality of the 'superhero landing', where a character lands with one knee, one fist, and a foot on the ground, which is hard on the knees and not advisable for real-life situations. He also explains kinetic energy, as seen in Black Panther's suit, which absorbs and stores the energy from bullets to use later. The concept of recoil is introduced with Wonder Woman's deflecting of bullets, which in reality would result in minimal impact due to the low mass and high velocity of bullets.
💥 Analyzing Superhero Strength and Terminal Velocity
The script continues with an analysis of Superman's ability to lift a building, suggesting that increasing the contact area would be necessary for such a feat. It then moves on to Spider-Man's web strength, explaining that the force exerted by the webs may not be enough to hold a boat together. The Iron Man suit's micro thruster rockets are proposed as a more effective solution. The section concludes with Captain America's terminal velocity, describing how he reaches a constant speed during a fall due to the balance of gravitational force and air resistance, and how adjusting his body position can affect his falling speed.
🤔 The Physics of Superhero Actions and Reactions
This paragraph delves into the concept of net force as demonstrated by Iron Man's strategy to prevent a chain of people from falling. It also touches on the disintegration effect seen in 'The Boys', questioning the physics behind a character running through another. The Incredibles' scene of running on water is critiqued, suggesting that rapid foot movement would be required to generate enough force to counteract gravity. Lastly, Iron Man's flight is discussed, highlighting the importance of thruster placement for stability.
🛡️ Superhero Protection and the Science of Impact
The script examines Groot's ability to protect others by creating a rigid sphere, suggesting that a crumple zone could absorb impact better. It also discusses the concept of force pairs, as seen in 'The Defenders', where super-strong characters must consider the direction of their punches to avoid being propelled backward. The paragraph concludes with a brief look at Superman's X-ray vision, pondering the scientific plausibility of such an ability.
⚔️ The Physics of Superhero Combat and Windup
In this final paragraph, the focus is on the physics of combat, particularly Captain America's use of Thor's hammer in 'Avengers Endgame'. The windup motion before swinging the hammer is analyzed to explain how it increases the hammer's speed and thus the impact force. The summary acknowledges the entertainment value of unrealistic physics in superhero movies, suggesting that complete realism might detract from the fun.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Superhero Landing
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Recoil
💡Contact Area
💡Tensile Strength
💡Terminal Velocity
💡Net Force
💡X-ray Vision
💡Impact Force
💡Force Pairs
💡Windup
Highlights
Superhero landings are visually impressive but hard on the knees and impractical compared to normal landing techniques.
Force distribution during landing can be optimized by increasing the stopping distance, as seen in parachute landing falls.
Kinetic energy, as demonstrated by Black Panther's suit, is a concept that can be used to store and release energy from moving objects.
Recoil is the equal and opposite reaction to a force exerted, affecting both the shooter and the bullet in firearms.
Superman's lifting of a building is physically implausible due to the structural integrity and force distribution issues.
Spider-Man's web strength is limited by the material's tensile strength and the force needed to prevent an object from falling apart.
Terminal velocity is the constant speed reached during free fall when air resistance equals gravitational force.
Captain America's water entry technique in 'The Winter Soldier' maximizes depth penetration to decrease stopping force.
In a chain of people hanging, the force required increases exponentially with each additional person.
A-Train's high-speed collision in 'The Boys' raises questions about the physical effects of such impacts on both parties.
Running on water, as seen in 'The Incredibles', would require rapid and forceful impacts with the water's surface.
Iron Man's flight stability is enhanced by the positioning of thrusters above the center of mass.
Groot's protective cage in 'Guardians of the Galaxy' could function as a crumple zone to absorb impact forces.
Force pairs, as illustrated in 'The Defenders', mean that the force exerted by one object is met with an equal and opposite force.
X-ray vision, as portrayed in 'Man of Steel', would theoretically allow Superman to see through objects due to the penetrating nature of X-rays.
Captain America's windup with Thor's hammer in 'Avengers Endgame' increases the hammer's speed and impact force.
The importance of physics in movies is highlighted, even if not entirely accurate, for the sake of entertainment and storytelling.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Dr. Michio Kaku Answers Physics Questions From Twitter | Tech Support | WIRED

Mythology Expert Reviews Greek & Roman Mythology in Movies (Part 1) | Vanity Fair

Brian Cox on how black holes could unlock the mysteries of our universe

Niayesh Afshordi: Reflections on Spacetime

Energy, Forces and Movement | FULL EPISODE COMPILATION | Science Max
Conservation of Linear Momentum
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: