Why was Turkey Neutral in WW2?
TLDRThis historical overview details Turkey's strategic neutrality during World War II, contrasting its non-involvement with its active role in World War I as part of the Ottoman Empire. The script highlights Turkey's efforts to avoid conflict, focusing instead on internal affairs and diplomacy. Despite pressure from both the Axis and Allied powers, Turkey maintained its stance, providing supplies to both sides until it was clear the Axis was losing. It eventually declared war on Germany and Japan symbolically and became one of the original members of the United Nations. The video also mentions the sponsorship of Surfshark VPN, emphasizing online privacy protection.
Takeaways
- 🕊️ Turkey's primary goal during World War II was to maintain neutrality and avoid direct involvement in the conflict.
- 🌏 Geographically, Turkey was positioned favorably, not being directly between the Axis and Allied powers, which allowed for a more neutral stance.
- 🤝 Turkey received bids to join the war from both sides but focused on internal affairs as a newly established republic.
- 🛡️ The script mentions SurfsharkVPN as a sponsor, emphasizing online privacy protection and security against threats like trackers and malware.
- 🏰 Historically, Turkey (then the Ottoman Empire) had a different approach in World War I, aligning with the Central Powers and suffering significant territorial losses post-war.
- 🏛️ The Treaty of Sèvres in 1920 and subsequent Turkish War of Independence led to the abolition of the Ottoman Sultanate and the establishment of the Republic of Turkey.
- 🔧 Mustafa Kemal Atatürk became the first president of Turkey, leading the transformation from a monarchical empire to a modern nation-state.
- 🤔 Ismet Inönü, Atatürk's successor, faced early pressures from Britain and France to form alliances against a potential German threat.
- 📜 The Anglo-Franco-Turkish mutual aid agreement required military support from France and Britain in exchange for Turkey's neutrality.
- ⏳ Turkey's neutrality was strategic, providing supplies to both Axis and Allies until it was clear the Axis was losing, prompting a shift in allegiance.
- 🎖️ In the final stages of the war, Turkey declared war on Germany and Japan symbolically and became one of the original members of the United Nations.
- 🛡️ Turkey's military was ill-prepared and outdated, which contributed to their decision to remain neutral for as long as possible.
Q & A
What was Turkey's primary goal during World War II?
-Turkey's primary goal during World War II was to stay out of the conflict and focus on its internal affairs.
How was Turkey's position during World War II different from its stance in World War I?
-In World War I, Turkey, as part of the Ottoman Empire, quickly aligned with the Central Powers and entered the conflict. In contrast, during World War II, Turkey pursued a policy of neutrality and focused on not getting involved in the war.
What was the significance of the Treaty of Sevres for Turkey?
-The Treaty of Sevres, signed in 1920, marked the beginning of the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire and led to the relinquishment of most of its territories. It was followed by a war of independence and the establishment of the Republic of Turkey.
Who was the first president of the Republic of Turkey, and when was it established?
-Mustafa Kemal Atatürk was elected as the first president of the Republic of Turkey, which was established on October 29, 1923.
What was the role of Ismet Inönü after Atatürk's death?
-Ismet Inönü became Atatürk's successor and the president of Turkey after Atatürk's death on November 10, 1938. He faced the global issues brewing at the time and had to navigate Turkey's position during the early stages of World War II.
What was the mutual aid pact between Turkey, France, and Britain, and what were its terms?
-The mutual aid pact was an agreement created in the fall of 1938, where France and Britain were required to help Turkey receive military necessities and provide a loan for other commodities. In return, Turkey was to remain neutral unless the war spread past the northern European vicinity.
Why did Turkey not join the war when Italy entered it on June 10th, 1940?
-Turkey chose to remain neutral despite the mutual aid agreement with the Allies because it was surrounded by potential threats and believed that joining the fight against Italy and the Axis powers would have led to an immediate defeat.
What was the significance of the German-Turkish Friendship Treaty formed on June 18th?
-The German-Turkish Friendship Treaty allowed Germany to focus on their Russian opponents while assuring Turkey that they were not at risk of an attack from the Germans, which they had feared since the invasion of Poland in 1939.
Why did Turkey cut all remaining ties with the Axis powers in August 1944?
-By April 1944, it was evident that the Axis powers were losing the war. This prompted Turkey to cut all remaining ties with those nations, including the diplomatic relationship formed through the German-Turkish Friendship Treaty.
What actions did Turkey take in February and March of 1945 regarding World War II?
-In February 1945, Turkey attended the inaugural meeting of the United Nations. In March, Turkey declared war on both Germany and Japan, marking the end of Turkish neutrality in World War II, although no Turkish troops were actually sent into battle.
How did Turkey's military situation compare to its stance in World War I?
-Turkey's military was poorly prepared during World War II, with outdated equipment from World War I. This situation was a wise choice as it prevented full belligerence and allowed Turkey to maintain neutrality until it was strategically beneficial to do otherwise.
What were the economic benefits for Turkey due to its actions during World War II?
-Turkey benefited economically from its actions during the war, most notably by being paid for the chromium it sold to Germany. Unlike German-occupied or allied nations, Turkey did not suffer economic losses due to the war.
Outlines
🕊️ Turkey's Neutrality and Posture in World War II
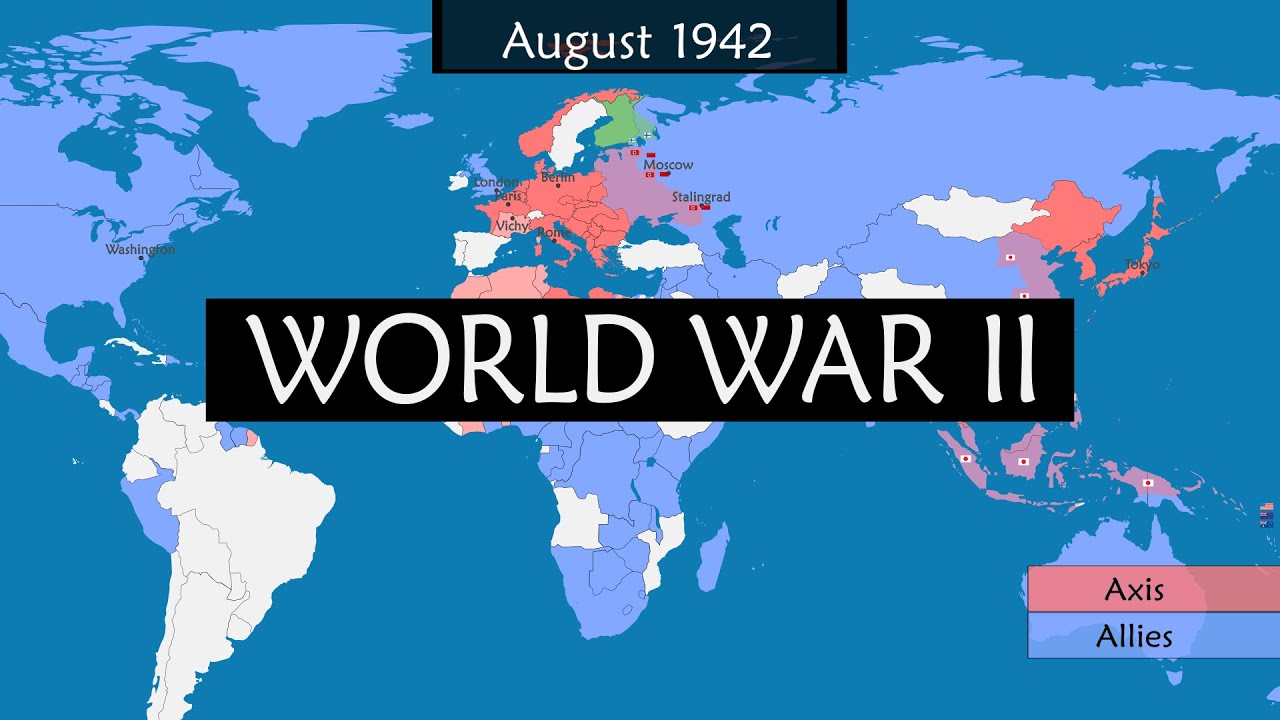
This paragraph discusses Turkey's strategic decision to remain neutral during World War II, mirroring the global desire for peace following the atrocities of World War II. It highlights Turkey's geographical advantage and its focus on internal affairs rather than joining either the Axis or Allied powers. The script also introduces the sponsor, SurfsharkVPN, emphasizing online privacy and security. Additionally, it contrasts Turkey's approach in World War II with its active involvement as the Ottoman Empire in World War I, which led to significant territorial losses and the empire's downfall. The paragraph concludes with the establishment of the Republic of Turkey and Ismet Inönü's ascension as president, navigating the complex geopolitical landscape leading up to World War II.
🤝 Turkey's Diplomatic Maneuvers and Military Preparedness
The second paragraph delves into Turkey's diplomatic efforts to maintain neutrality during World War II. It outlines the mutual aid agreement with France and Britain, which required military and financial support in exchange for Turkey's potential alliance. The rapid defeat of France, however, complicated Turkey's position, leading to a reevaluation of alliances. Despite initial commitments, Turkey chose to remain neutral, especially with the expansion of the war into the Mediterranean. The paragraph also describes Turkey's strategic non-aggression pact with Germany, which allowed both nations to focus on other fronts. Throughout the war, Turkey provided supplies to both Axis and Allied powers until it became clear that the Axis was losing, prompting Turkey to sever ties. The paragraph concludes with Turkey's symbolic declaration of war against Germany and Japan and its attendance at the inaugural United Nations meeting, reflecting a shift in its diplomatic stance.
🎖️ Turkey's Post-War Position and Strategic Neutrality
The final paragraph summarizes Turkey's post-war status and the benefits of its strategic neutrality. It details Turkey's military strength at the outset of World War II, noting the outdated equipment and the small size of its armed forces. Despite pressure to join the war, Turkey's declarations of war were more political statements than military commitments. The paragraph highlights Turkey's economic gains from selling chromium to Germany and its status as one of the 51 original members of the United Nations. It concludes by reflecting on President Ismet Inönü's positive legacy and Turkey's successful navigation of World War II, which allowed the nation to emerge in a stronger position than after World War I.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡World War II
💡Ismet Inonu
💡Neutrality
💡United Nations
💡Chromium
💡Treaty of Sevres
💡Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
💡Anglo-Franco-Turkish Mutual Aid Pact
💡Axis Powers
💡Allies
Highlights
Turkey's goal during WWII was to maintain neutrality and focus on internal affairs.
Sponsor SurfsharkVPN promotes online privacy protection with its VPN service.
Turkey's strategic geographical positioning during WWII allowed it to avoid direct conflict.
Efforts from both Axis and Allied sides to persuade Turkey into the war were unsuccessful.
Turkey's military was poorly prepared with outdated equipment from WWI.
Turkey's decision in WWI to align with Central Powers led to its downfall.
The Treaty of Sevres marked the beginning of the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire.
Turkey's War of Independence resulted in the abolition of the Ottoman Sultanate.
The Republic of Turkey was established with Mustafa Kamal Atatürk as its first president.
Ismet Inönü succeeded Atatürk and faced early pressure from Britain and France.
Turkey signed a mutual aid agreement with France and Britain in 1938.
Turkey remained neutral as the war spread to Northern Europe, per the mutual aid pact.
Turkey's breach of the mutual aid agreement was justified by unmet promises from Allies.
Turkey formed a friendship treaty with Germany in June 1941 for mutual non-aggression.
Turkey provided supplies like chromium to both Germany and the Allies until 1944.
Turkey cut ties with Axis powers in August 1944 as their defeat became evident.
Turkey joined the United Nations in 1945 and declared war on Germany and Japan symbolically.
Turkey's economic benefit from selling chromium to Germany contrasted with occupied nations.
President Ismet Inönü's leadership in maintaining neutrality is positively remembered.
Turkey's strategic neutrality allowed it to recover better than after WWI.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: